Poor prognosis of hexokinase 2 overexpression in solid tumors of digestive system: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 28415659
- PMCID: PMC5458288
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15974
Poor prognosis of hexokinase 2 overexpression in solid tumors of digestive system: a meta-analysis
Abstract
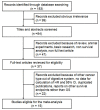
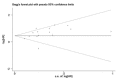
Several previous studies have reported the prognostic value of hexokinase 2 (HK2) in digestive system tumors. However, these studies were limited by the small sample sizes and the results were inconsistent among them. Therefore, we conducted a meta-analysis based on 15 studies with 1932 patients to assess the relationship between HK2 overexpression and overall survival (OS) of digestive system malignancies. The relationship of HK2 and clinicopathological features was also evaluated. Hazard ratio (HR) or odds ratio (OR) with its 95% confidence intervals (CI) were calculated to estimate the effect size. Positive HK2 expression showed poor OS in all tumor types (HR = 1.75 [1.41-2.18], P < 0.001). When stratified by tumor type, the impact of HK2 overexpression on poor prognosis was observed in gastric cancer (HR = 1.77 [1.25-2.50], P < 0.001), hepatocellular carcinoma (HR = 1.87 [1.58-2.21], P < 0.001), and colorectal cancer (HR = 2.89 [1.62-5.15], P < 0.001), but not in pancreatic ductal adencarcinoma (HR = 1.11 [0.58-2.11], P = 0.763). Furthermore, high HK2 expression was significantly associated with some phenotypes of tumor aggressiveness, such as large tumor size (OR = 2.03 [1.10-3.74], P = 0.024), positive lymph node metastasis (OR = 2.05 [1.39-3.02], P < 0.001), advanced clinical stage (OR = 2.17 [1.21-3.89], P = 0.009) and high alpha fetoprotein level (OR = 1.47 [1.09-2.02] P = 0.013). In summary, HK2 might act as a prognostic indicator and a potential therapeutic target of these digestive system cancers.
Keywords: digestive system; hexokinase 2; meta-analysis; prognosis; solid tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Prognostic Significance of the Metabolic Marker Hexokinase-2 in Various Solid Tumors: A Meta-Analysis.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 8;11(11):e0166230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166230. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27824926 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Value of Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR as a Novel Biomarker in Digestive Cancers: A Meta-Analysis.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jan 1;17:1533034618756783. doi: 10.1177/1533034618756783. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29444619 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of synergistic hexokinase-2 and beta2-adrenergic receptor expression in human hepatocelluar carcinoma after curative resection.BMC Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun 3;16(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12876-016-0474-8. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27255554 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic potential of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR expression in human digestive system carcinomas: A meta-analysis.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jul;234(7):10926-10933. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27918. Epub 2018 Dec 19. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30569489
-
Clinical value of octamer-binding transcription factor 4 as a prognostic marker in patients with digestive system cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Mar;32(3):567-576. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13624. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 28320060
Cited by
-
Expression of HK2, PKM2, and PFKM Is Associated with Metastasis and Late Disease Onset in Breast Cancer Patients.Genes (Basel). 2022 Mar 20;13(3):549. doi: 10.3390/genes13030549. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328104 Free PMC article.
-
Potential of Novel Methyl Jasmonate Analogs as Anticancer Agents to Metabolically Target HK-2 Activity in Glioblastoma Cells.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 23;13:828400. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.828400. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35677429 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the Novel PFKFB3 Inhibitor KAN0438757 on Colorectal Cancer Cells and Its Systemic Toxicity Evaluation In Vivo.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Feb 28;13(5):1011. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051011. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33671096 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of Hexokinases II-Mediated Glycolysis Contributes to Piperlongumine-Induced Tumor Suppression in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells.Int J Biol Sci. 2019 Mar 1;15(4):826-837. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.31749. eCollection 2019. Int J Biol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30906213 Free PMC article.
-
Merging metabolic modeling and imaging for screening therapeutic targets in colorectal cancer.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2025 Jan 28;11(1):12. doi: 10.1038/s41540-025-00494-1. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2025. PMID: 39875420 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

