Auranofin radiosensitizes tumor cells through targeting thioredoxin reductase and resulting overproduction of reactive oxygen species
- PMID: 28415723
- PMCID: PMC5482612
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16113
Auranofin radiosensitizes tumor cells through targeting thioredoxin reductase and resulting overproduction of reactive oxygen species
Abstract
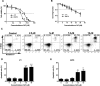
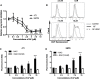
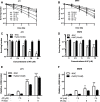
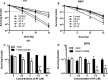
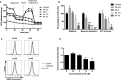
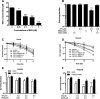
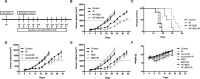
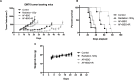
Auranofin (AF) is an anti-arthritic drug considered for combined chemotherapy due to its ability to impair the redox homeostasis in tumor cells. In this study, we asked whether AF may in addition radiosensitize tumor cells by targeting thioredoxin reductase (TrxR), a critical enzyme in the antioxidant defense system operating through the reductive protein thioredoxin. Our principal findings in murine 4T1 and EMT6 tumor cells are that AF at 3-10 μM is a potent radiosensitizer in vitro, and that at least two mechanisms are involved in TrxR-mediated radiosensitization. The first one is linked to an oxidative stress, as scavenging of reactive oxygen species (ROS) by N-acetyl cysteine counteracted radiosensitization. We also observed a decrease in mitochondrial oxygen consumption with spared oxygen acting as a radiosensitizer under hypoxic conditions. Overall, radiosensitization was accompanied by ROS overproduction, mitochondrial dysfunction, DNA damage and apoptosis, a common mechanism underlying both cytotoxic and antitumor effects of AF. In tumor-bearing mice, a simultaneous disruption of the thioredoxin and glutathione systems by the combination of AF and buthionine sulfoximine was shown to significantly improve tumor radioresponse. In conclusion, our findings illuminate TrxR in cancer cells as an exploitable radiobiological target and warrant further validation of AF in combination with radiotherapy.
Keywords: ROS; auranofin; buthionine sulfoximine; radiosensitization; thioredoxin reductase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting redox homeostasis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells: GSH-depleting agents enhance auranofin-induced cell death.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Oct 5;8(10):e3067. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.412. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28981107 Free PMC article.
-
Auranofin, an inhibitor of thioredoxin reductase, induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells by generation of reactive oxygen species.Gen Physiol Biophys. 2017 Apr;36(2):117-128. doi: 10.4149/gpb_2016043. Epub 2017 Feb 20. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2017. PMID: 28218611
-
Selenadiazole derivatives as potent thioredoxin reductase inhibitors that enhance the radiosensitivity of cancer cells.Eur J Med Chem. 2014 Sep 12;84:335-42. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.07.032. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Eur J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 25036792
-
Inhibition of Thioredoxin-Reductase by Auranofin as a Pro-Oxidant Anticancer Strategy for Glioblastoma: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 27;26(5):2084. doi: 10.3390/ijms26052084. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40076706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Anticancer Activity of Auranofin.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2019;67(3):186-191. doi: 10.1248/cpb.c18-00767. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2019. PMID: 30827998 Review.
Cited by
-
Thioredoxin System Protein Expression in Carcinomas of the Pancreas, Distal Bile Duct, and Ampulla in the United Kingdom.Diseases. 2024 Sep 24;12(10):227. doi: 10.3390/diseases12100227. Diseases. 2024. PMID: 39452470 Free PMC article.
-
Glutathione levels are associated with methotrexate resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines.Front Oncol. 2022 Dec 1;12:1032336. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1032336. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36531023 Free PMC article.
-
TRIAP1 knockdown sensitizes non-small cell lung cancer to ionizing radiation by disrupting redox homeostasis.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Apr;11(4):1015-1025. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13358. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32096592 Free PMC article.
-
Ferroptosis: Frenemy of Radiotherapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 25;25(7):3641. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073641. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond gold: the chemoenhancing mechanism and therapeutic potential of auranofin in melanoma.Cancer Biol Med. 2025 Jun 27;22(6):672-89. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2025.0026. Cancer Biol Med. 2025. PMID: 40579895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trachootham D, Alexandre J, Huang P. Targeting cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic approach? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:579–591. - PubMed
-
- Iwasawa S, Yamano Y, Takiguchi Y, Tanzawa H, Tatsumi K, Uzawa K. Upregulation of thioredoxin reductase 1 in human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2011;25:637–644. - PubMed
-
- Kakolyris S, Giatromanolaki A, Koukourakis M, Powis G, Souglakos J, Sivridis E, Georgoulias V, Gatter KC, Harris AL. Thioredoxin expression is associated with lymph node status and prognosis in early operable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:3087–3091. - PubMed
-
- Porporato PE, Payen VL, Perez-Escuredo J, De Saedeleer CJ, Danhier P, Copetti T, Dhup S, Tardy M, Vazeille T, Bouzin C, Feron O, Michiels C, Gallez B, et al. A mitochondrial switch promotes tumor metastasis. Cell Rep. 2014;8:754–766. - PubMed
-
- Kim SY, Kim SJ, Kim BJ, Rah SY, Chung SM, Im MJ, Kim UH. Doxorubicin-induced reactive oxygen species generation and intracellular Ca2+ increase are reciprocally modulated in rat cardiomyocytes. Exp Mol Med. 2006;38:535–545. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

