Binding of galectin-1 to integrin β1 potentiates drug resistance by promoting survivin expression in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 28415760
- PMCID: PMC5482619
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16208
Binding of galectin-1 to integrin β1 potentiates drug resistance by promoting survivin expression in breast cancer cells
Abstract
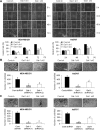
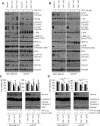
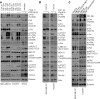
Galectin-1 is a β-galactoside binding protein secreted by many types of aggressive cancer cells. Although many studies have focused on the role of galectin-1 in cancer progression, relatively little attention has been paid to galectin-1 as an extracellular therapeutic target. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying galectin-1-mediated cancer progression, we established galectin-1 knock-down cells via retroviral delivery of short hairpin RNA (shRNA) against galectin-1 in two triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines, MDA-MB-231 and Hs578T. Ablation of galectin-1 expression decreased cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and doxorubicin resistance. We found that these effects were caused by decreased galectin-1-integrin β1 interactions and suppression of the downstream focal adhesion kinase (FAK)/c-Src pathway. We also found that silencing of galectin-1 inhibited extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling, thereby down-regulating survivin expression. This finding implicates STAT3 as a transcription factor for survivin. Finally, rescue of endogenous galectin-1 knock-down and recombinant galectin-1 treatment both recovered signaling through the FAK/c-Src/ERK/STAT3/survivin pathway. Taken together, these results suggest that extracellular galectin-1 contributes to cancer progression and doxorubicin resistance in TNBC cells. These effects appear to be mediated by galectin-1-induced up-regulation of the integrin β1/FAK/c-Src/ERK/STAT3/survivin pathway. Our results imply that extracellular galectin-1 has potential as a therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer.
Keywords: STAT3; drug resistance; galectin-1; integrin β1; survivin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
STAT3 as a potential therapeutic target in triple negative breast cancer: a systematic review.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 14;38(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1206-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31088482 Free PMC article.
-
3,4-Methylenedioxy-β-nitrostyrene inhibits adhesion and migration of human triple-negative breast cancer cells by suppressing β1 integrin function and surface protein disulfide isomerase.Biochimie. 2015 Mar;110:81-92. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2015.01.006. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Biochimie. 2015. PMID: 25593085
-
Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in the tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cell: a new role for G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in mediating tamoxifen resistance through cancer-associated fibroblast-derived fibronectin and β1-integrin signaling pathway in tumor cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 May 21;17(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0579-y. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25990368 Free PMC article.
-
Stat3/Oct-4/c-Myc signal circuit for regulating stemness-mediated doxorubicin resistance of triple-negative breast cancer cells and inhibitory effects of WP1066.Int J Oncol. 2018 Jul;53(1):339-348. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4399. Epub 2018 May 8. Int J Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29750424
-
Stress-induced EGF receptor signaling through STAT3 and tumor progression in triple-negative breast cancer.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Aug 15;451:24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.01.013. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28088463 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of galectins in cancer: Biological challenges for their clinical application.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1104625. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1104625. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36703969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STAT3 as a potential therapeutic target in triple negative breast cancer: a systematic review.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 May 14;38(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1206-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31088482 Free PMC article.
-
Galectins in Cancer and the Microenvironment: Functional Roles, Therapeutic Developments, and Perspectives.Biomedicines. 2021 Sep 4;9(9):1159. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9091159. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34572346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prodigiosin/PU-H71 as a novel potential combined therapy for triple negative breast cancer (TNBC): preclinical insights.Sci Rep. 2020 Sep 7;10(1):14706. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71157-w. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32895397 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Based Therapeutics: Current Developments in Targeted Molecular Therapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Oct 15;13(10):1694. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13101694. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34683988 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, Andre F, Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B, Green M, Cristofanilli M, Hortobagyi GN, Pusztai L. Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1275–81. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.4147. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barondes SH, Castronovo V, Cooper DN, Cummings RD, Drickamer K, Feizi T, Gitt MA, Hirabayashi J, Hughes C, Kasai K, et al. Galectins: a family of animal beta-galactoside-binding lectins. Cell. 1994;76:597–8. doi. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

