Signal transduction growth factors: the effective governance of transcription and cellular adhesion in cancer invasion
- PMID: 28415812
- PMCID: PMC5482705
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16300
Signal transduction growth factors: the effective governance of transcription and cellular adhesion in cancer invasion
Abstract
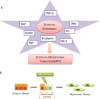
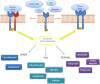
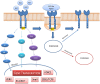
Giulio Bizzozero classified the tissues concerning their capacity to self-renew during the adult life in labile, stable and permanent tissues. In 1940 Viktor Hamburger and Rita Levi Montalcini exposed the possibility to induce the growth of permanent cells thanks to a specific ligand Nerve Growth Factor (NGF). Stanley Cohen purified a protein the Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF), able to induce epidermis proliferation and to elicit precocious eye disclosure and teeth eruption, establishing the "inverse" relationships between the proliferation and differentiation. These two biological effects induced by EGF were according to EGFR signaling is involved in a large array of cellular functions such as proliferation, survival, adhesion, migration and differentiation. This review is focused on the key role of growth factors signaling and their downstream effectors in physiological and in pathological phenomena, the authors highlight the governance of Growth factors during the EMT in cancer invasion.
Keywords: EGFR TGFβ; KGF; cancer invasion; e-cadherin; phosphorylation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Snail regulated by PKC/GSK-3β pathway is crucial for EGF-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of cancer cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2014 Nov;358(2):491-502. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1953-2. Epub 2014 Aug 16. Cell Tissue Res. 2014. PMID: 25124796
-
LIM-domain proteins in transforming growth factor β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and myofibroblast differentiation.Cell Signal. 2012 Apr;24(4):819-25. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.12.004. Epub 2011 Dec 11. Cell Signal. 2012. PMID: 22182513 Review.
-
A ROS/STAT3/HIF-1α signaling cascade mediates EGF-induced TWIST1 expression and prostate cancer cell invasion.Prostate. 2014 May;74(5):528-36. doi: 10.1002/pros.22776. Epub 2014 Jan 16. Prostate. 2014. PMID: 24435707
-
CD44 enhances the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in association with colon cancer invasion.Int J Oncol. 2012 Jul;41(1):211-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2012.1453. Epub 2012 Apr 30. Int J Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22552741
-
Regulation of EMT by TGFβ in cancer.FEBS Lett. 2012 Jul 4;586(14):1959-70. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.02.037. Epub 2012 Feb 28. FEBS Lett. 2012. PMID: 22710176 Review.
Cited by
-
The Crosstalk between Prostate Cancer and Microbiota Inflammation: Nutraceutical Products Are Useful to Balance This Interplay?Nutrients. 2020 Aug 31;12(9):2648. doi: 10.3390/nu12092648. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32878054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression level of EGFR and MET receptors regulates invasiveness of melanoma cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Dec;23(12):8453-8463. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14730. Epub 2019 Oct 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31638339 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Osteosarcoma.Biomolecules. 2023 Feb 20;13(2):398. doi: 10.3390/biom13020398. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 36830767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Curcumin in Prostate Cancer Cells and Derived Spheroids.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jul 9;14(14):3348. doi: 10.3390/cancers14143348. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884410 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNAs modulate tumor microenvironment to promote metastasis: novel avenue for therapeutic intervention.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jun 13;11:1164301. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1164301. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37384249 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cohen S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962;237:1555–62. - PubMed
-
- Covelli I, Rossi R, Mozzi R, Frati L. Synthesis of bioactive 131 I-labeled epidermal growth factor and its distribution in rat tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1972;27:225–30. - PubMed
-
- Frati L, Daniele S, Delogu A, Covelli I. Selective binding of the epidermal growth factor and its specific effects on the epithelial cells of the cornea. Exp Eye Res. 1972;14:135–41. - PubMed
-
- Covelli I, Mozzi R, Rossi R, Frati L. The mechanism of action of the epidermal growth factor. 3. Stimulation of the uptake of labeled precursors into RNA, DNA and proteins induced by EGF in isolated tumor cells. Hormones. 1972;3:183–91. - PubMed
-
- Carpenter G, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:7709–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

