Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of cancer
- PMID: 28415828
- PMCID: PMC5503661
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16379
Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of cancer
Abstract
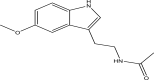
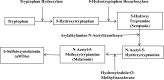
The epidemiological studies have indicated a possible oncostatic property of melatonin on different types of tumors. Besides, experimental studies have documented that melatonin could exert growth inhibition on some human tumor cells in vitro and in animal models. The underlying mechanisms include antioxidant activity, modulation of melatonin receptors MT1 and MT2, stimulation of apoptosis, regulation of pro-survival signaling and tumor metabolism, inhibition on angiogenesis, metastasis, and induction of epigenetic alteration. Melatonin could also be utilized as adjuvant of cancer therapies, through reinforcing the therapeutic effects and reducing the side effects of chemotherapies or radiation. Melatonin could be an excellent candidate for the prevention and treatment of several cancers, such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, gastric cancer and colorectal cancer. This review summarized the anticancer efficacy of melatonin, based on the results of epidemiological,experimental and clinical studies, and special attention was paid to the mechanisms of action.
Keywords: anticancer; apoptosis; mechanisms of action; melatonin; receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ekmekcioglu C. Melatonin receptors in humans: Biological role and clinical relevance. Biomed Pharmacother. 2006;60:97–108. - PubMed
-
- Li AN, Xu XR, Li S, Guo YJ, Liu JL, Li HB. Secretion and bioactivity of melatonin. Int J Mod Biol Med. 2012;1:21–39.
-
- Stehle JH, Saade A, Rawashdeh O, Ackermann K, Jilg A, Sebestény T, Maronde E. A survey of molecular details in the human pineal gland in the light of phylogeny, structure, function and chronobiological diseases. J Pineal Res. 2011;51:17–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources