Pentoxifylline plus ACEIs/ARBs for proteinuria and kidney function in chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 28415944
- PMCID: PMC5536675
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060516663094
Pentoxifylline plus ACEIs/ARBs for proteinuria and kidney function in chronic kidney disease: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective This meta-analysis aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of pentoxifylline (PTF) plus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs)/angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) for proteinuria and kidney function in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Methods CENTRAL, EMBASE, Ovid-MEDLINE, PubMed, and CNKI were searched for relevant, randomized, controlled trials (RCTs). A meta-analysis was performed to review the effect of PTF plus ACEIs/ARBs vs. ACEIs/ARBs alone on proteinuria and kidney function in CKD. Results Eleven RCTs including 705 patients were retrieved. PTF plus ACEI/ARB treatment significantly decreased proteinuria in patients with CKD within 6 months (standard mean difference [SMD] -0.52; 95% CI -0.90 to 0.15; I2 = 68%) and significantly attenuated a decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) in patients with stages 3-5 CKD after 6 months of treatment (standard mean difference [SMD] 0.30; confidence limit [Cl] 95% CI 0.06 to 0.54; I2 = 0%). PTF plus ACEIs/ARBs for 9 to 12 months significantly reduced albuminuria in patients with CKD (SMD-0.30, 95% CI -0.57 to 0.03; I2 = 0%) and alleviated the decline in eGFR in patients with stages 3-5 CKD (SMD 0.51; 95% CI 0.06 to 0.96; I2 = 61%). Conclusion The combination of an ACEI or ARB and PTF has a protective effect in reducing proteinuria by ameliorating the decline in eGFR in patients with stages 3-5 CKD.
Keywords: ACEI/ARB; Pentoxifylline; chronic kidney disease; meta-analysis.
Figures
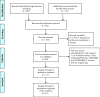
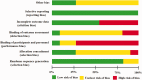
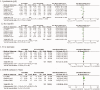
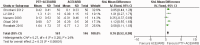

Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of combining pentoxifylline with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker in diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2015 May;47(5):815-22. doi: 10.1007/s11255-015-0968-2. Epub 2015 Apr 11. Int Urol Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25862237 Review.
-
Is Chronic Kidney Disease Progression Influenced by the Type of Renin-Angiotensin-System Blocker Used?Nephron. 2019;143(2):100-107. doi: 10.1159/000500925. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Nephron. 2019. PMID: 31203280
-
Can Pentoxifylline be used as Adjunct Therapy to ACE Inhibitors and ARBs in Preserving Kidney Function?J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2016;19(1):1-7. doi: 10.18433/J3K020. J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2016. PMID: 27096690 Review.
-
Renoprotective effect of combining pentoxifylline with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II receptor blocker in advanced chronic kidney disease.J Formos Med Assoc. 2014 Apr;113(4):219-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Feb 7. J Formos Med Assoc. 2014. PMID: 24512756
-
Efficacy and Safety of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors in Combination with Angiotensin-Receptor Blockers in Nondiabetic Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(38):7961-7973. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210614120552. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34126881
Cited by
-
Obesity-related glomerulopathy: How it happens and future perspectives.Diabet Med. 2025 Jun;42(6):e70042. doi: 10.1111/dme.70042. Epub 2025 Apr 14. Diabet Med. 2025. PMID: 40226862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Inflammation in Diabetic Kidney Disease: Is There a Role for Pentoxifylline?Kidney360. 2020 Feb 28;1(4):292-299. doi: 10.34067/KID.0001252019. eCollection 2020 Apr 30. Kidney360. 2020. PMID: 35372914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparing the Effect of Folic Acid and Pentoxifylline on Delaying Dialysis Initiation in Patients with Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2019 Sep 12;11(9):2192. doi: 10.3390/nu11092192. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31547288 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of pentoxifylline on oxidative renal cell injury associated with renal crystal formation in a hyperoxaluric rat model.Urolithiasis. 2019 Oct;47(5):415-424. doi: 10.1007/s00240-018-1072-8. Epub 2018 Jul 6. Urolithiasis. 2019. PMID: 29980797
-
Therapeutic Insights in Chronic Kidney Disease Progression.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 23;8:645187. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.645187. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33708784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Carney EF. Epidemiology: global burden of disease study 2013 reports that disability caused by CKD is increasing worldwide. Nat Rev Nephrol 2015; 11: 446–446. - PubMed
-
- Indridason OS, Thorsteinsdóttir I, Pálsson R. Advances in detection, evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Laeknabladid 2007; 93: 201–207. [in Icelandic, English Abstract]. - PubMed
-
- Barnett AH, Bain SC, Bouter P, et al. Angiotensin-receptor blockade versus converting-enzyme inhibition in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1952–1961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

