Dusuqing granules (DSQ) suppress inflammation in Klebsiella pneumonia rat via NF-κB/MAPK signaling
- PMID: 28415997
- PMCID: PMC5392945
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1736-x
Dusuqing granules (DSQ) suppress inflammation in Klebsiella pneumonia rat via NF-κB/MAPK signaling
Abstract
Background: Dusuqing granules (DSQ) have been used in the treatment of bacterial pneumonia clinically, with remarkable benefits. This study was initiated to explore the effects of DSQ on pulmonary inflammation by regulating nuclear factor (NF)-κB/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling in bacterial pneumonia rats.
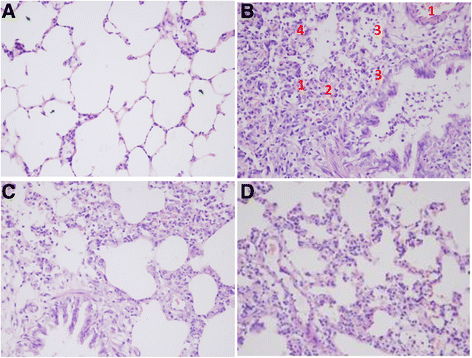
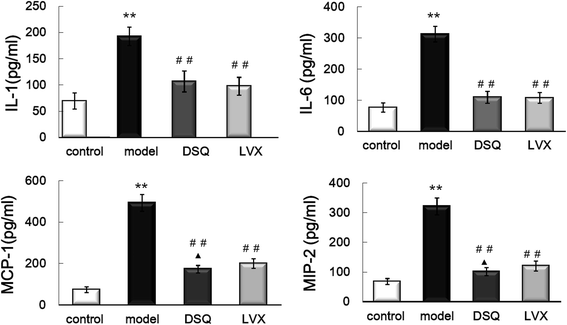
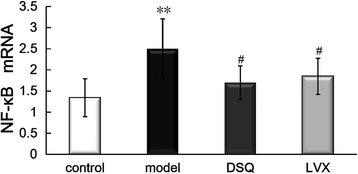
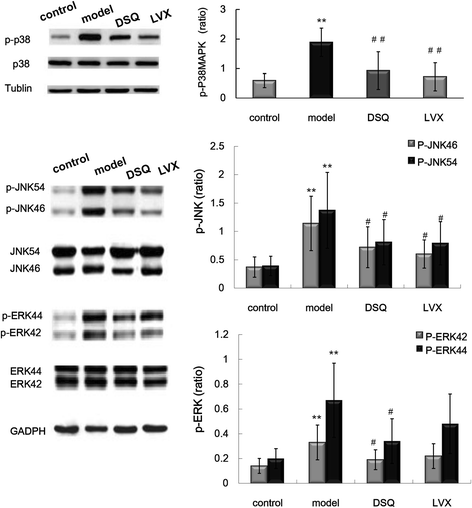
Methods: Rat model was duplicated with Klebsiella pneumonia by a one-time intratracheal injection. Rats were randomized into control, model, DSQ and levofloxacin (LVX) groups. After administrated with appropriate medicines for 7 days, lung tissues were harvested and prepared for pathological analysis, and interleukin (IL)-1, IL-6, monocyte chemotactic protein (MCP)-1and macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-2 detections. NF-κB mRNA was measured by real-time qPCR, and the phosphorylation and total proteins of P38MAPK, JNK46/54, ERK42/44 were determined by Western blotting.
Results: Marked pathological impairments were observed in model rats, whereas were improved in DSQ group. The cytokines levels, NF-κB mRNA expression and the phosphorylation of P38MAPK, JNK46/54 and ERK42/44 proteins were significantly higher in model group, and were significantly depressed in DSQ group.
Conclusion: The protective effects of DSQ on Klebsiella pneumonia might be attributed to its inactivative effects of NF-κB/ MAPK pathway.
Keywords: Dusuqing granules; Klebsiella pneumoniae pneumonia; NF-κB/MAPK pathway; Traditional Chinese medicine; inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Protection and mechanism of Fagopyrum cymosum on lung injury in rats with Klebsiella pneumonia].Zhong Yao Cai. 2012 Apr;35(4):603-7. Zhong Yao Cai. 2012. PMID: 23019909 Chinese.
-
Qingfei Litan decoction alleviated Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced pneumonia by targeting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB axis via miR-146a-5p.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jun 12;349:119947. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119947. Epub 2025 May 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40378935
-
Zerumbone from Zingiber zerumbet Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced ICAM-1 and Cytokines Expression via p38 MAPK/JNK-IκB/NF-κB Pathway in Mouse Model of Acute Lung Injury.Chin J Physiol. 2018 Jun;61(3):171-180. doi: 10.4077/CJP.2018.BAG562. Chin J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29962177
-
The regulatory effect and mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine on the renal inflammatory signal transduction pathways in diabetic kidney disease: A review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Sep 20;103(38):e39746. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039746. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39312356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent highlights of Chinese herbs in treatment of allergic disease: Acting via mitogen-activated protein kinase signal pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2017 Aug;23(8):570-573. doi: 10.1007/s11655-016-2526-x. Epub 2016 Jul 26. Chin J Integr Med. 2017. PMID: 27460493 Review.
Cited by
-
High Glucose Stimulates Expression of MFHAS1 to Mitigate Inflammation via Akt/HO-1 Pathway in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells.Inflammation. 2018 Mar;41(2):400-408. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0696-0. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29168081
-
Triptolide prevents bone loss via suppressing osteoclastogenesis through inhibiting PI3K-AKT-NFATc1 pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jun;24(11):6149-6161. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15229. Epub 2020 Apr 28. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32347017 Free PMC article.
-
A Matrine Derivative M54 Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis and Prevents Ovariectomy-Induced Bone Loss by Targeting Ribosomal Protein S5.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 30;9:22. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00022. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. Retraction in: Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 19;16:1575621. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1575621. PMID: 29441015 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Animal models of Klebsiella pneumoniae mucosal infections.Front Microbiol. 2024 Mar 15;15:1367422. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1367422. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38559342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trichosanthis Pericarpium Aqueous Extract Protects H9c2 Cardiomyocytes from Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Injury by Regulating PI3K/Akt/NO Pathway.Molecules. 2018 Sep 20;23(10):2409. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102409. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30241309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Holmes RB. Friedlander’s pneumonia. Am J Roentgenol Radium Therapy, Nucl Med. 1956;75:728–747. - PubMed
-
- Chuang TY, Lin CJ, Chi CL, Liu AY, Lee SW, Lin TL, Wang JT, Hsueh PR. Rapidly fatal bacteremic pneumonia caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae with K1 hypermucoviscosity phenotype in a previously healthy young man receiving levofloxacin treatment. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2009;42:439–441. - PubMed
-
- Kang H, Bang T-S, Lee J-W, Lew J-H, Eom SH, Lee K, Choi H-Y. Protective effect of the methanol extract from Cryptotaenia japonica Hassk Against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in vitro and in vivo. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012;12:199. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-S1-P199. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

