Patterns, Receptors, and Signals: Regulation of Phagosome Maturation
- PMID: 28416446
- PMCID: PMC5455985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2017.03.006
Patterns, Receptors, and Signals: Regulation of Phagosome Maturation
Abstract
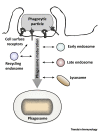
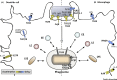
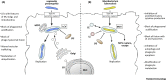
Recognition of microbial pathogens and dead cells and their phagocytic uptake by specialized immune cells are essential to maintain host homeostasis. Phagosomes undergo fusion and fission events with endosomal and lysosomal compartments, a process called 'phagosome maturation', which leads to the degradation of the phagosomal content. However, many phagocytic cells also act as antigen-presenting cells and must balance degradation and peptide preservation. Emerging evidence indicates that receptor engagement by phagosomal cargo, as well as inflammatory mediators and cellular activation affect many aspects of phagosome maturation. Unsurprisingly, pathogens have developed strategies to hijack this machinery, thereby interfering with host immunity. Here, we highlight progress in this field, summarize findings on the impact of immune signals, and discuss consequences for pathogen elimination.
Keywords: antigen presentation; host–pathogen interaction; immune response; inflammation; phagocytosis; phagosome maturation.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Cosson P., Soldati T. Eat, kill or die: when amoeba meets bacteria. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2008;11:271–276. - PubMed
-
- Levin R. The life cycle of phagosomes: formation, maturation, and resolution. Immunol. Rev. 2016;273:156–179. - PubMed
-
- Reimann H.A. Microbic phagocytosis by enteric epithelial cells. JAMA. 1965;192:1130–1132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

