NRF2 Induction Supporting Breast Cancer Cell Survival Is Enabled by Oxidative Stress-Induced DPP3-KEAP1 Interaction
- PMID: 28416489
- PMCID: PMC5464605
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2204
NRF2 Induction Supporting Breast Cancer Cell Survival Is Enabled by Oxidative Stress-Induced DPP3-KEAP1 Interaction
Abstract
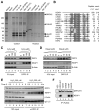
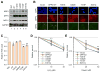
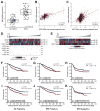
NRF2 is a transcription factor serving as a master regulator of the expression of many genes involved in cellular responses to oxidative and other stresses. In the absence of stress, NRF2 is constantly synthesized but maintained at low levels as it is targeted by KEAP1 for ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation. NRF2 binds KEAP1 mainly through a conserved "ETGE" motif that has also been found in several other proteins, such as DPP3, which has been shown to bind KEAP1 and enhance NRF2 function upon overexpression. Here we demonstrate the interaction between endogenous DPP3 and endogenous KEAP1. We further show that the DPP3-KEAP1 interaction is strongly induced by hydrogen peroxide and that DPP3 is required for timely NRF2 induction and nuclear accumulation in the estrogen receptor (ER)-positive MCF7 breast cancer cells. Moreover, we present evidence that the binding of DPP3 to KEAP1 stabilizes the latter. Finally, we show that DPP3 is overexpressed in breast cancer and that elevated levels of DPP3 mRNA correlate with increased NRF2 downstream gene expression and poor prognosis, particularly for ER-positive breast cancer. Our studies reveal novel insights into the regulation of NRF2 and identify DPP3 and an NRF2 transcriptional signature as potential biomarkers for breast cancer prognosis and treatment. Cancer Res; 77(11); 2881-92. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase 3 protects oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-injured hippocampal neurons by suppressing apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation via modulation of Keap1/Nrf2 signaling.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Jul;96:107595. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107595. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33812256
-
Proteomic analysis of ubiquitin ligase KEAP1 reveals associated proteins that inhibit NRF2 ubiquitination.Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 1;73(7):2199-210. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4400. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23382044 Free PMC article.
-
Acute expression of the transcription factor Nrf2 after treatment with quinolinic acid is not induced by oxidative stress in the rat striatum.Neurotoxicology. 2019 Jul;73:120-131. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Neurotoxicology. 2019. PMID: 30876764
-
The emerging role of dipeptidyl peptidase 3 in pathophysiology.FEBS J. 2023 May;290(9):2246-2262. doi: 10.1111/febs.16429. Epub 2022 Mar 25. FEBS J. 2023. PMID: 35278345 Review.
-
Canonical and non-canonical mechanisms of Nrf2 activation.Pharmacol Res. 2018 Aug;134:92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.06.013. Epub 2018 Jun 18. Pharmacol Res. 2018. PMID: 29913224 Review.
Cited by
-
Keap1-MCM3 interaction is a potential coordinator of molecular machineries of antioxidant response and genomic DNA replication in metazoa.Sci Rep. 2018 Aug 14;8(1):12136. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-30562-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30108253 Free PMC article.
-
NRF2 and Mitochondrial Function in Cancer and Cancer Stem Cells.Cells. 2022 Aug 4;11(15):2401. doi: 10.3390/cells11152401. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35954245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dexmedetomidine Relieves Neuropathic Pain in Rats With Chronic Constriction Injury via the Keap1-Nrf2 Pathway.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 8;9:714996. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.714996. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34568327 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative inhibition of sirtuin 6 by imidazole derivative triggers oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis associated with Nrf2/Keap1 signaling in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 3;14:1335305. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1335305. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38235110 Free PMC article.
-
The Metabolic Control of Myeloid Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cells. 2021 Oct 30;10(11):2960. doi: 10.3390/cells10112960. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831183 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

