In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Target Assessment of Eravacycline against Escherichia coli in a Murine Thigh Infection Model
- PMID: 28416552
- PMCID: PMC5487610
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00250-17
In Vivo Pharmacodynamic Target Assessment of Eravacycline against Escherichia coli in a Murine Thigh Infection Model
Abstract
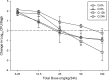
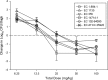
Eravacycline is a novel fluorocycline antibiotic with potent activity against a broad range of pathogens, including strains with tetracycline and other drug resistance phenotypes. The goal of the studies was to determine which pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) parameter and magnitude best correlated with efficacy in the murine thigh infection model. Six Escherichia coli isolates were utilized for the studies. MICs were determined using CLSI methods and ranged from 0.125 to 0.25 mg/liter. A neutropenic murine thigh infection model was utilized for all treatment studies. Single-dose plasma pharmacokinetics were determined in mice after administration of 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40, and 80 mg/kg of body weight. Pharmacokinetic studies exhibited maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) values of 0.34 to 2.58 mg/liter, area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) from time zero to infinity (AUC0-∞) values of 2.44 to 57.6 mg · h/liter, and elimination half-lives of 3.9 to 17.6 h. Dose fractionation studies were performed using total drug doses of 6.25 mg/kg to 100 mg/kg fractionated into 6-, 8-, 12-, or 24-h regimens. Nonlinear regression analysis demonstrated that the 24-h free drug AUC/MIC (fAUC/MIC) was the PK/PD parameter that best correlated with efficacy (R2 = 0.80). In subsequent studies, we used the neutropenic murine thigh infection model to determine if the magnitude of the AUC/MIC needed for the efficacy of eravacycline varied among pathogens. Mice were treated with 2-fold increasing doses (range, 3.125 to 50 mg/kg) of eravacycline every 12 h. The mean fAUC/MIC magnitudes associated with the net stasis and the 1-log-kill endpoints were 27.97 ± 8.29 and 32.60 ± 10.85, respectively.
Keywords: Escherichia coli; eravacycline; pharmacodynamics.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



References
-
- Solomkin JS, Ramesh MK, Cesnauskas G, Novikovs N, Stefanova P, Sutcliffe JA, Walpole SM, Horn PT. 2014. Phase 2, randomized, double-blind study of the efficacy and safety of two dose regimens of eravacycline versus ertapenem for adult community-acquired complicated intra-abdominal infections. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:1847–1854. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01614-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wada K, Uehara S, Yamamoto M, Sadahira T, Mitsuhata R, Araki M, Kobayashi Y, Ishii A, Kariyama R, Watanabe T, Nasu Y, Kumon H. 2016. Clinical analysis of bacterial strain profiles isolated from urinary tract infections: a 30-year study. J Infect Chemother 22:478–482. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2016.04.004. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

