Terbinafine Resistance of Trichophyton Clinical Isolates Caused by Specific Point Mutations in the Squalene Epoxidase Gene
- PMID: 28416557
- PMCID: PMC5487658
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00115-17
Terbinafine Resistance of Trichophyton Clinical Isolates Caused by Specific Point Mutations in the Squalene Epoxidase Gene
Abstract
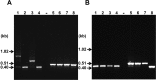
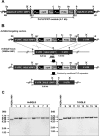
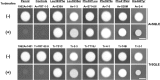
Terbinafine is one of the allylamine antifungal agents whose target is squalene epoxidase (SQLE). This agent has been extensively used in the therapy of dermatophyte infections. The incidence of patients with tinea pedis or unguium tolerant to terbinafine treatment prompted us to screen the terbinafine resistance of all Trichophyton clinical isolates from the laboratory of the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois collected over a 3-year period and to identify their mechanism of resistance. Among 2,056 tested isolates, 17 (≈1%) showed reduced terbinafine susceptibility, and all of these were found to harbor SQLE gene alleles with different single point mutations, leading to single amino acid substitutions at one of four positions (Leu393, Phe397, Phe415, and His440) of the SQLE protein. Point mutations leading to the corresponding amino acid substitutions were introduced into the endogenous SQLE gene of a terbinafine-sensitive Arthroderma vanbreuseghemii (formerly Trichophyton mentagrophytes) strain. All of the generated A. vanbreuseghemii transformants expressing mutated SQLE proteins exhibited obvious terbinafine-resistant phenotypes compared to the phenotypes of the parent strain and of transformants expressing wild-type SQLE proteins. Nearly identical phenotypes were also observed in A. vanbreuseghemii transformants expressing mutant forms of Trichophyton rubrum SQLE proteins. Considering that the genome size of dermatophytes is about 22 Mb, the frequency of terbinafine-resistant clinical isolates was strikingly high. Increased exposure to antifungal drugs could favor the generation of resistant strains.
Keywords: Trichophyton; antifungal resistance; dermatophytes; reverse genetics approach; squalene epoxidase; terbinafine.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High terbinafine resistance in Trichophyton interdigitale isolates in Delhi, India harbouring mutations in the squalene epoxidase gene.Mycoses. 2018 Jul;61(7):477-484. doi: 10.1111/myc.12772. Epub 2018 Apr 27. Mycoses. 2018. PMID: 29577447
-
Increased terbinafine resistance among clinical genotypes of Trichophyton mentagrophytes/T. interdigitale species complex harboring squalene epoxidase gene mutations.J Mycol Med. 2024 Sep;34(3):101495. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2024.101495. Epub 2024 Jun 16. J Mycol Med. 2024. PMID: 38896927
-
Terbinafine-Resistant Dermatophytes Isolated in Japan.Med Mycol J. 2025;66(1):11-15. doi: 10.3314/mmj.24-00020. Med Mycol J. 2025. PMID: 40024788
-
The Emerging Terbinafine-Resistant Trichophyton Epidemic: What Is the Role of Antifungal Susceptibility Testing?Dermatology. 2022;238(1):60-79. doi: 10.1159/000515290. Epub 2021 May 31. Dermatology. 2022. PMID: 34058736 Review.
-
[Terbinafine-resistant dermatophytoses and onychomycosis due to Trichophyton rubrum].Hautarzt. 2021 Oct;72(10):868-877. doi: 10.1007/s00105-021-04879-1. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Hautarzt. 2021. PMID: 34459941 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Synergistic Effects of Efflux Pump Modulators on the Azole Antifungal Susceptibility of Microsporum canis.Mycopathologia. 2020 Apr;185(2):279-288. doi: 10.1007/s11046-019-00419-7. Epub 2020 Jan 1. Mycopathologia. 2020. PMID: 31894500
-
NP213 (Novexatin®): A unique therapy candidate for onychomycosis with a differentiated safety and efficacy profile.Med Mycol. 2020 Nov 10;58(8):1064-1072. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myaa015. Med Mycol. 2020. PMID: 32232410 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of E-test and CLSI methods for Itraconazole, Fluconazole and Ketoconazole susceptibilities of Microsporum canis strains.Mycopathologia. 2020 Jun;185(3):495-502. doi: 10.1007/s11046-020-00453-w. Epub 2020 May 28. Mycopathologia. 2020. PMID: 32468154
-
Antifungal Drug Susceptibility Testing of Dermatophytes: Laboratory Findings to Clinical Implications.Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019 May-Jun;10(3):225-233. doi: 10.4103/idoj.IDOJ_146_19. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2019. PMID: 31149563 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Resistance Mechanism in a Terbinafine-Resistant Strain of Microsporum canis.Mycopathologia. 2018 Jun;183(3):623-627. doi: 10.1007/s11046-018-0242-0. Epub 2018 Jan 16. Mycopathologia. 2018. PMID: 29340910
References
-
- Reiss E, Shadomy HJ, Lyon GM. 2011. Fundamental medical mycology, p 527–565. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken, NJ.
-
- Reiss E, Shadomy HJ, Lyon GM. 2011. Fundamental medical mycology, p 75–105. Wiley-Blackwell, Hoboken, NJ.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

