A Kinase-Independent Role for Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 19 in p53 Response
- PMID: 28416637
- PMCID: PMC5472832
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00626-16
A Kinase-Independent Role for Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 19 in p53 Response
Abstract
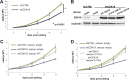
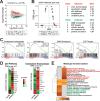
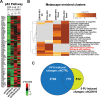
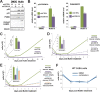
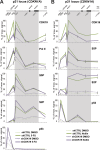
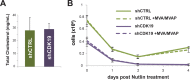
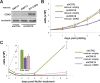
The human Mediator complex regulates RNA polymerase II transcription genome-wide. A general factor that regulates Mediator function is the four-subunit kinase module, which contains either cyclin-dependent kinase 8 (CDK8) or CDK19. Whereas CDK8 is linked to specific signaling cascades and oncogenesis, the cellular roles of its paralog, CDK19, are poorly studied. We discovered that osteosarcoma cells (SJSA) are naturally depleted of CDK8 protein. Whereas stable CDK19 knockdown was tolerated in SJSA cells, proliferation was reduced. Notably, proliferation defects were rescued upon the reexpression of wild-type or kinase-dead CDK19. Comparative RNA sequencing analyses showed reduced expression of mitotic genes and activation of genes associated with cholesterol metabolism and the p53 pathway in CDK19 knockdown cells. SJSA cells treated with 5-fluorouracil, which induces metabolic and genotoxic stress and activates p53, further implicated CDK19 in p53 target gene expression. To better probe the p53 response, SJSA cells (shCDK19 versus shCTRL) were treated with the p53 activator nutlin-3. Remarkably, CDK19 was required for SJSA cells to return to a proliferative state after nutlin-3 treatment, and this effect was kinase independent. These results implicate CDK19 as a regulator of p53 stress responses and suggest a role for CDK19 in cellular resistance to nutlin-3.
Keywords: 5-FU; 5-fluorouracil; CDK19; CDK8; Mediator kinase; RNA-Seq; SJSA; cholesterol; cortistatin A; drug resistance; nutlin; nutlin-3; osteosarcoma; p53; stress; transcription.
Copyright © 2017 Audetat et al.
Figures



References
-
- Daniels DL, Ford M, Schwinn MK, Benink H, Galbraith MD, Amunugama R, Jones R, Allen D, Okazaki N, Yamakawa H, Miki F, Nagase T, Espinosa JM, Urh M. 2013. Mutual exclusivity of MED12/MED12L, MED13/13L, and CDK8/19 paralogs revealed within the CDK-Mediator kinase module. J Proteomics Bioinform S2:004.
-
- Pelish HE, Liau BB, Nitulescu II, Tangpeerachaikul A, Poss ZC, Da Silva DH, Caruso BT, Arefolov A, Fadeyi O, Christie AL, Du K, Banka D, Schneider EV, Jestel A, Zou G, Si C, Ebmeier CC, Bronson RT, Krivtsov AV, Myers AG, Kohl NE, Kung AL, Armstrong SA, Lemieux ME, Taatjes DJ, Shair MD. 2015. Mediator kinase inhibition further activates super-enhancer-associated genes in AML. Nature 526:273–276. doi: 10.1038/nature14904. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
