Economic inequality increases risk taking
- PMID: 28416655
- PMCID: PMC5422783
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1616453114
Economic inequality increases risk taking
Abstract
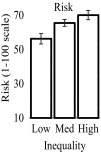
Rising income inequality is a global trend. Increased income inequality has been associated with higher rates of crime, greater consumer debt, and poorer health outcomes. The mechanisms linking inequality to poor outcomes among individuals are poorly understood. This research tested a behavioral account linking inequality to individual decision making. In three experiments (n = 811), we found that higher inequality in the outcomes of an economic game led participants to take greater risks to try to achieve higher outcomes. This effect of unequal distributions on risk taking was driven by upward social comparisons. Next, we estimated economic risk taking in daily life using large-scale data from internet searches. Risk taking was higher in states with greater income inequality, an effect driven by inequality at the upper end of the income distribution. Results suggest that inequality may promote poor outcomes, in part, by increasing risky behavior.
Keywords: decision making; income inequality; inequality; risk taking; socioeconomic status.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors acknowledge funding from the Spencer Foundation.
Figures





Comment in
-
Reply to van Hoorn: Social comparisons of "enough" are an informational signal.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jun 20;114(25):E4900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1707044114. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28607040 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Informational content of relative deprivation as a channel linking economic inequality to risk taking.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jun 20;114(25):E4899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1706625114. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28607041 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Saez E, Zucman G. Wealth inequality in the United States since 1913: Evidence from capitalized income tax data. Q J Econ. 2016;131:519–578.
-
- Choe J. Income inequality and crime in the United States. Econ Lett. 2008;101:31–33.
-
- Freund E, Morris I. Gambling and income inequality in the states. Policy Stud J. 2006;34:265–276.
-
- Frank R. Falling Behind: How Rising Inequality Harms the Middle Class. Univ of California Press; Berkeley, CA: 2013.
-
- Kawachi I, Subramanian SV. 2014. Income inequality. Social Epidemiology, eds Berkman LF, Kawachi I, Glymour M (Oxford Univ Press, New York), 126–152.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

