Theranostic imaging of liver cancer using targeted optical/MRI dual-modal probes
- PMID: 28416757
- PMCID: PMC5464824
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15642
Theranostic imaging of liver cancer using targeted optical/MRI dual-modal probes
Abstract
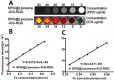
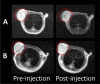
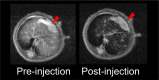
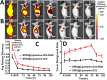
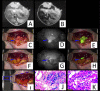
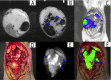
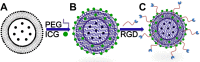
The accurate preoperative detection and intraoperative navigation afforded by imaging techniques have had significant impact on the success of liver cancer surgeries. However, it is difficult to achieve satisfactory performance in both diagnosis and surgical treatment processes using any single modality imaging method. Here, we report the synthesis and characteristics of a novel dual-modality magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and near-infrared fluorescence (NIRF) probe and verify its feasibility in nude mouse models with liver cancer. The probes are comprised of superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) nanoparticles coated with liposomes to which a tumor-targeted agent, Arg-Gly-Asp peptides (RGD), and a NIRF dye (indocyanine green, ICG) have been conjugated. Specific targeting, biodistribution, and the imaging ability of the probes for MRI-NIRF were examined. Furthermore, we applied the dual-modality methodology toward the preoperative diagnosis and intraoperative guidance of radical resection in mouse models with both orthotopic liver tumors and intrahepatic tumor metastasis. The study demonstrated that both MRI and fluorescent images showed clear tumor delineation after probe injection (SPIO@Liposome-ICG-RGD). The contrast-to-noise ratio obtained from MRI was 31.9 ± 25.4 at post-injection for the preoperative diagnosis, which is helpful for detecting small tumors (0.9 ± 0.5 mm). The maximum tumor to background ratio of NIRF imaging was 2.5 ± 0.3 at 72 h post-injection for effectively capturing miniscule tumor lesions (0.6 ± 0.3 mm) intraoperatively. The novel MRI-NIRF dual modality probes are promising for the achievement of more accurate liver tumor detection and resection.
Keywords: MRI/optical; dual-modality; intraoperative navigation; liver cancer; preoperative diagnosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NIRF Optical/PET Dual-Modal Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Heptamethine Carbocyanine Dye.Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2018 Mar 8;2018:4979746. doi: 10.1155/2018/4979746. eCollection 2018. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29706843 Free PMC article.
-
CD146-targeted immunoPET and NIRF Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma with a Dual-Labeled Monoclonal Antibody.Theranostics. 2016 Aug 8;6(11):1918-33. doi: 10.7150/thno.15568. eCollection 2016. Theranostics. 2016. PMID: 27570560 Free PMC article.
-
A novel plectin/integrin-targeted bispecific molecular probe for magnetic resonance/near-infrared imaging of pancreatic cancer.Biomaterials. 2018 Nov;183:173-184. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.08.048. Epub 2018 Aug 26. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 30172243
-
Quicker, deeper and stronger imaging: A review of tumor-targeted, near-infrared fluorescent dyes for fluorescence guided surgery in the preclinical and clinical stages.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020 Jul;152:123-143. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2020.05.002. Epub 2020 May 8. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020. PMID: 32437752 Review.
-
Fluorescence imaging in the surgical management of liver cancers: Current status and future perspectives.Asian J Surg. 2022 Jul;45(7):1375-1382. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2021.08.063. Epub 2021 Oct 13. Asian J Surg. 2022. PMID: 34656410 Review.
Cited by
-
The theranostic efficiency of tumor-specific, pH-responsive, peptide-modified, liposome-containing paclitaxel and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Mar 13;13:1495-1504. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S157082. eCollection 2018. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29559778 Free PMC article.
-
Near-infrared fluorescence imaging with indocyanine green for assessment of donor livers in a rat model of ischemia-reperfusion.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Jan 20;22(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02103-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35057742 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically Encoded Self-Assembling Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as a Possible Platform for Cancer-Cell Tracking.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Mar 16;13(3):397. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13030397. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 33809789 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous enhancement of T1 and T2 magnetic resonance imaging of liver tumor at respective low and high magnetic fields.Theranostics. 2022 Jan 1;12(1):410-417. doi: 10.7150/thno.67155. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 34987653 Free PMC article.
-
Recent developments in multimodality fluorescence imaging probes.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018 May;8(3):320-338. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2018.03.010. Epub 2018 Mar 30. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2018. PMID: 29881672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- American Cancer Society Global Cancer Facts & Figures. (3) 2012 http://www.cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/global.
-
- American Cancer Society Cancer Facts & Figures. 2013 http://www.cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/global.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

