Large-scale analyses of common and rare variants identify 12 new loci associated with atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 28416818
- PMCID: PMC5585859
- DOI: 10.1038/ng.3843
Large-scale analyses of common and rare variants identify 12 new loci associated with atrial fibrillation
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Large-scale analyses of common and rare variants identify 12 new loci associated with atrial fibrillation.Nat Genet. 2017 Jul 27;49(8):1286. doi: 10.1038/ng0817-1286c. Nat Genet. 2017. PMID: 28747752 No abstract available.
Abstract
Atrial fibrillation affects more than 33 million people worldwide and increases the risk of stroke, heart failure, and death. Fourteen genetic loci have been associated with atrial fibrillation in European and Asian ancestry groups. To further define the genetic basis of atrial fibrillation, we performed large-scale, trans-ancestry meta-analyses of common and rare variant association studies. The genome-wide association studies (GWAS) included 17,931 individuals with atrial fibrillation and 115,142 referents; the exome-wide association studies (ExWAS) and rare variant association studies (RVAS) involved 22,346 cases and 132,086 referents. We identified 12 new genetic loci that exceeded genome-wide significance, implicating genes involved in cardiac electrical and structural remodeling. Our results nearly double the number of known genetic loci for atrial fibrillation, provide insights into the molecular basis of atrial fibrillation, and may facilitate the identification of new potential targets for drug discovery.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Ellinor is the PI on a grant from Bayer HealthCare to the Broad Institute focused on the genetics and therapeutics of atrial fibrillation. The remaining authors have no disclosures.
Figures
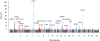

References
-
- January CT, et al. 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS Guideline for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:2246–2280. - PubMed
-
- Gudbjartsson DF, et al. Variants conferring risk of atrial fibrillation on chromosome 4q25. Nature. 2007;448:353–357. - PubMed
Online methods references
-
- Pe’er I, Yelensky R, Altshuler D, Daly MJ. Estimation of the multiple testing burden for genomewide association studies of nearly all common variants. Genet Epidemiol. 2008;32:381–385. - PubMed
-
- Hoggart CJ, Clark TG, De Iorio M, Whittaker JC, Balding DJ. Genome-wide significance for dense SNP and resequencing data. Genet Epidemiol. 2008;32:179–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HL138737/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL111314/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 HL114724/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K24 HL105780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092217/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL092577/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018522/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128914/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090620/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_U127561128/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- UM1 CA182913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

