Predictive Factors of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection in Elderly Patients with Community-Onset Pneumonia
- PMID: 28416961
- PMCID: PMC5392492
- DOI: 10.4046/trd.2017.80.2.201
Predictive Factors of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection in Elderly Patients with Community-Onset Pneumonia
Abstract
Background: Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection is a severe and life-threatening disease in patients with community-onset (CO) pneumonia. However, the current guidelines lack specificity for a screening test for MRSA infection.
Methods: This study was retrospectively conducted in elderly patients aged ≥65 years, who had contracted CO-pneumonia during hospitalization at the Jeju National University Hospital, between January 2012 and December 2014. We analyzed the risk factors of MRSA in these patients and developed a scoring system to predict MRSA infection.
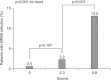
Results: A total of 762 patients were enrolled in this study, including 19 (2.4%) with MRSA infection. Healthcare-associated pneumonia (HCAP) showed more frequent MRSA infection compared to community-acquired pneumonia (4.4% vs. 1.5%, respectively; p=0.016). In a multivariate logistic regression analysis, admissions during the influenza season (odds ratio [OR], 2.896; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.022-8.202; p=0.045), chronic kidney disease (OR, 3.555; 95% CI, 1.157-10.926; p=0.027), and intensive care unit admission (OR, 3.385; 95% CI, 1.035-11.075; p=0.044) were identified as predictive factors for MRSA infection. However, the presence of HCAP was not significantly associated with MRSA infection (OR, 1.991; 95% CI, 0.720-5.505; p=0.185). The scoring system consisted of three variables based on the multivariate analysis, and showed moderately accurate diagnostic prediction (area under curve, 0.790; 95% CI, 0.680-0.899; p<0.001).
Conclusion: MRSA infection would be considered in elderly CO-pneumonia patients, with three risk factors identified herein. When managing elderly patients with pneumonia, clinicians might keep in mind that these risk factors are associated with MRSA infection, which may help in selecting appropriate antibiotics.
Keywords: Community-Acquired Infections; Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus; Mortality; Pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article are reported.
Figures

References
-
- Kwong JC, Chua K, Charles PG. Managing severe community-acquired pneumonia due to community methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2012;14:330–338. - PubMed
-
- Rubinstein E, Kollef MH, Nathwani D. Pneumonia caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Infect Dis. 2008;46(Suppl 5):S378–S385. - PubMed
-
- Lobo LJ, Reed KD, Wunderink RG. Expanded clinical presentation of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Chest. 2010;138:130–136. - PubMed
-
- Kalil AC, Metersky ML, Klompas M, Muscedere J, Sweeney DA, Palmer LB, et al. Management of adults with hospital-acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia: 2016 clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;63:e61–e111. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

