Comparison of intrathecal versus intra-articular dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to bupivacaine on postoperative pain following knee arthroscopy: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 28416997
- PMCID: PMC5392657
- DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2017.30.2.134
Comparison of intrathecal versus intra-articular dexmedetomidine as an adjuvant to bupivacaine on postoperative pain following knee arthroscopy: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Postoperative pain is a common, distressing symptom following arthroscopic knee surgery. The aim of this study was to compare the potential analgesic effect of dexmedetomidine after intrathecal versus intra-articular administration following arthroscopic knee surgery.
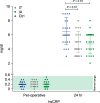
Methods: Ninety patients undergoing unilateral elective arthroscopic knee surgery were randomly assigned into three groups in a double-blind placebo controlled study. The intrathecal dexmedetomidine group (IT) received an intrathecal block with intrathecal dexmedetomidine, the intra-articular group (IA) received an intrathecal block and intra-articular dexmedetomidine, and the control group received an intrathecal block and intra-articular saline. The primary outcome of our study was postoperative pain as assessed by the visual analogue scale of pain (VAS). Secondary outcomes included the effect of dexmedetomidine on total postoperative analgesic use and time to the first analgesic request, hemodynamics, sedation, postoperative nausea and vomiting, patient satisfaction, and postoperative C-reactive protein (CRP) levels.
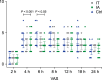
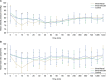
Results: Dexmedetomidine administration decreased pain scores for 4 h in both the intrathecal and intra-articular groups, compared to only 2 h in the control patient group. Furthermore, there was a significant reduction in pain scores for 6 h in the intra-articular group. The time to the first postoperative analgesia request was longer in the intra-articular group compared to the intrathecal and control groups. The total meperidine requirement was significantly lower in the intra-articular and intrathecal groups than in the control group.
Conclusions: Both intrathecal and intra-articular dexmedetomidine enhanced postoperative analgesia after arthroscopic knee surgery. Less total meperidine was required with intra-articular administration to extend postoperative analgesia to 6 h with hemodynamic stability.
Keywords: Arthroscopic knee surgery; Bupivacaine; Dexmedetomidine; Intra-articular; Intrathecal; Postoperative analgesia.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have no conflicts of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of intra-articular dexmedetomidine on postoperative analgesia after arthroscopic knee surgery.Br J Anaesth. 2008 Sep;101(3):395-9. doi: 10.1093/bja/aen184. Epub 2008 Jun 20. Br J Anaesth. 2008. PMID: 18567675 Clinical Trial.
-
Dexamethasone and Dexmedetomidine as an Adjuvant to Intraarticular Bupivacaine for Postoperative Pain Relief in Knee Arthroscopic Surgery: A Randomized Trial.Pain Physician. 2017 Nov;20(7):671-680. Pain Physician. 2017. PMID: 29149146 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Study Between Dexmedetomidine and Fentanyl as an Adjuvant to Intraarticular Bupivacaine for Postoperative Analgesia after Knee Arthroscopy.Pain Physician. 2021 Nov;24(7):E989-E996. Pain Physician. 2021. PMID: 34704709 Clinical Trial.
-
Intra-articular dexmedetomidine in knee arthroscopy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 6;8(1):4089. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22482-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29511256 Free PMC article.
-
Postsurgical analgesic efficacy by the intra-articular administration of ropivacaine with dexmedetomidine versus simple ropivacaine in patients undergoing knee arthroscopy.Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2024 May-Jun;68(3):306-312. doi: 10.1016/j.recot.2022.12.001. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 36567063 Review. English, Spanish.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Efficacy of Intra-Articular Plain Bupivacaine and Bupivacaine with Adjuvants (Dexmedetomidine and Magnesium Sulfate) for Postoperative Analgesia in Arthroscopic Knee Surgeries: A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Trial.Anesth Essays Res. 2018 Oct-Dec;12(4):848-854. doi: 10.4103/aer.AER_153_18. Anesth Essays Res. 2018. PMID: 30662119 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Intra-articular Dexmedetomidine on Postoperative Pain after Knee Arthroscopic Surgery.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2022 Mar;10(3):272-277. doi: 10.22038/ABJS.2021.53942.2706. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2022. PMID: 35514766 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intra-articular dexmedetomidine on experimental osteoarthritis in rats.PLoS One. 2021 Jan 12;16(1):e0245194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245194. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33434210 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Evaluation of Intra-articular Bupivacaine vs Bupivacaine and Dexmedetomidine for Postoperative Analgesia in Arthroscopic Knee Surgeries.Cureus. 2023 Aug 23;15(8):e43956. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43956. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37746467 Free PMC article.
-
Usefulness of patellar cartilage cross-sectional area for knee tibiofemoral osteoarthritis in elderly.Clin Interv Aging. 2019 Jun 5;14:1021-1026. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S205027. eCollection 2019. Clin Interv Aging. 2019. PMID: 31239652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bondok RS, Abd El-Hady AM. Intra-articular magnesium is effective for postoperative analgesia in arthroscopic knee surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2006;97:389–392. - PubMed
-
- Abdallah FW, Dwyer T, Chan VW, Niazi AU, Ogilvie-Harris DJ, Oldfield S, et al. IV and Perineural dexmedetomidine similarly prolong the duration of analgesia after interscalene brachial plexus block: a randomized, three-arm, triple-masked, placebo-controlled trial. Anesthesiology. 2016;124:683–695. - PubMed
-
- Kanazi GE, Aouad MT, Jabbour-Khoury SI, Al Jazzar MD, Alameddine MM, Al-Yaman R, et al. Effect of low-dose dexmedetomidine or clonidine on the characteristics of bupivacaine spinal block. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006;50:222–227. - PubMed
-
- Al-Mustafa MM, Abu-Halaweh SA, Aloweidi AS, Murshidi MM, Ammari BA, Awwad ZM, et al. Effect of dexmedetomidine added to spinal bupivacaine for urological procedures. Saudi Med J. 2009;30:365–370. - PubMed
-
- Al-Ghanem SM, Massad IM, Al-Mustafa MM, Al-Zaben KR, Qudaisat IY, Qatawneh AM, et al. Effect of adding dexmedetomidine versus fentanyl to intrathecal bupivacaine on spinal block characteristics in gynecological procedures: a double blind controlled study. Am J Appl Sci. 2009;6:882–887.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

