Association of gene coding variation and resting metabolic rate in a multi-ethnic sample of children and adults
- PMID: 28417008
- PMCID: PMC5381071
- DOI: 10.1186/s40608-017-0145-5
Association of gene coding variation and resting metabolic rate in a multi-ethnic sample of children and adults
Abstract
Background: Resting metabolic rates (RMR) vary across individuals. Understanding the determinants of RMR could provide biological insight into obesity and its metabolic consequences such as type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
Methods: The present study measured RMR using reference standard indirect calorimetry and evaluated genetic variations from an exome array in a sample of children and adults (N = 262) predominantly of African and European ancestry with a wide range of ages (10 - 67 years old) and body mass indices (BMI; 16.9 - 56.3 kg/m2 for adults, 15.1 - 40.6 kg/m2 for children).
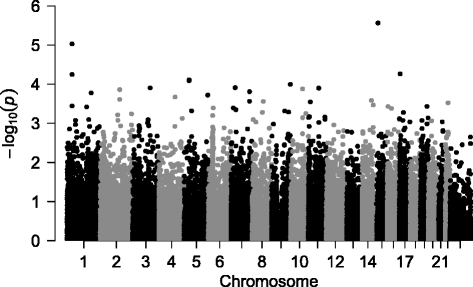
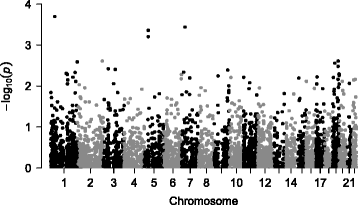
Results: Single variant analysis for RMR identified suggestive loci on chromosomes 15 (rs74010762, TRPM1, p-value = 2.7 × 10-6), 1 (rs2358728 and rs2358729, SH3D21, p-values < 5.8x10-5), 17 (AX-82990792, DHX33, 5.5 × 10-5) and 5 (rs115795863 and rs35433829, C5orf33 and RANBP3L, p-values < 8.2 × 10-5). To evaluate the effect of low frequency variations with RMR, we performed gene-based association tests. Our most significant locus was SH3D21 (p-value 2.01 × 10-4), which also contained suggestive results from single-variant analyses. A further investigation of all variants within the reported genes for all obesity-related loci from the GWAS catalog found nominal evidence for association of body mass index (BMI- kg/m2)-associated loci with RMR, with the most significant p-value at rs35433754 (TNKS, p-value = 0.0017).
Conclusions: These nominal associations were robust to adjustment for BMI. The most significant variants were also evaluated using phenome-wide association to evaluate pleiotropy, and genetically predicted gene expression using the summary statistics implicated loci related to in obesity and body composition. These results merit further examination in larger cohorts of children and adults.
Keywords: Gene-based analysis; Genetic variants; Obesity; Predicted gene expression; Resting metabolic rate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diet, physical activity and behavioural interventions for the treatment of overweight or obese children from the age of 6 to 11 years.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 22;6(6):CD012651. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012651. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28639319 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Incentives for preventing smoking in children and adolescents.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 6;6(6):CD008645. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008645.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28585288 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Interventions to change the behaviour of health professionals and the organisation of care to promote weight reduction in children and adults with overweight or obesity.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 30;11(11):CD000984. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000984.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 29190418 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
RMR-Related MAP2K6 Gene Variation on the Risk of Overweight/Obesity in Children: A 3-Year Panel Study.J Pers Med. 2021 Feb 2;11(2):91. doi: 10.3390/jpm11020091. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33540643 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing reveals SH3D21 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 3;20(4):e0302766. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0302766. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40179068 Free PMC article.
-
Comorbidity of Novel CRHR2 Gene Variants in Type 2 Diabetes and Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 29;23(17):9819. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179819. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077219 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-scale CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screening reveals SH3D21 as a sensitizer for gemcitabine.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 16;9(1):19188. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55893-2. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31844142 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-deficient mouse model established by CRISPR/Cas9 system reveals 15 reproductive organ-enriched genes dispensable for male fertility.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 May 21;12:1411162. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1411162. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38835510 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bosy-Westphal A, Wolf A, Buhrens F, Hitze B, Czech N, Monig H, Selberg O, Settler U, Pfeuffer M, Schrezenmeir J, et al. Familial influences and obesity-associated metabolic risk factors contribute to the variation in resting energy expenditure: the Kiel obesity prevention study. Am J Clin Nutr. 2008;87(6):1695–1701. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources