Chemical biology reveals CARF as a positive regulator of canonical Wnt signaling by promoting TCF/β-catenin transcriptional activity
- PMID: 28417011
- PMCID: PMC5387711
- DOI: 10.1038/celldisc.2017.3
Chemical biology reveals CARF as a positive regulator of canonical Wnt signaling by promoting TCF/β-catenin transcriptional activity
Abstract
Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates multiple biological processes and aberration of this pathway is frequently observed in human cancers. Previously, we uncovered NC043 as a small-molecule inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Here, we identified CARF as the cellular target of NC043. We found that NC043 binds directly to CARF through forming a covalent bond with the Cys-516 residue of CARF. Further study revealed that CARF interacts with Dvl, which potentiates the Dvl-c-Jun-β-catenin-TCF transcriptional complex and thus promotes Wnt signaling activation. NC043 could disrupt the interaction between CARF and Dvl, thereby impairing Wnt signal transduction. In line with this, knockdown of CARF in zebrafish leads to impairment of embryonic development, hematopoietic stem cell generation and caudal fin regeneration. Collectively, we identified CARF as the cellular target of NC043 and revealed CARF as a positive regulator of Wnt/β-catenin signal transduction.
Keywords: CARF; NC043; Wnt signaling; chemical biology; small molecule.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




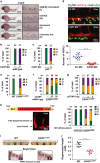
References
-
- Clevers H . Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in development and disease. Cell 2006; 127: 469–480. - PubMed
-
- Klaus A , Birchmeier W . Wnt signalling and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2008; 8: 387–398. - PubMed
-
- Wang S , Yin J , Chen D et al. Small-molecule modulation of Wnt signaling via modulating the Axin-LRP5/6 interaction. Nat Chem Biol 2013; 9: 579–585. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

