Collagen IV and basement membrane at the evolutionary dawn of metazoan tissues
- PMID: 28418331
- PMCID: PMC5395295
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.24176
Collagen IV and basement membrane at the evolutionary dawn of metazoan tissues
Abstract
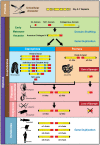
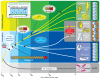
The role of the cellular microenvironment in enabling metazoan tissue genesis remains obscure. Ctenophora has recently emerged as one of the earliest-branching extant animal phyla, providing a unique opportunity to explore the evolutionary role of the cellular microenvironment in tissue genesis. Here, we characterized the extracellular matrix (ECM), with a focus on collagen IV and its variant, spongin short-chain collagens, of non-bilaterian animal phyla. We identified basement membrane (BM) and collagen IV in Ctenophora, and show that the structural and genomic features of collagen IV are homologous to those of non-bilaterian animal phyla and Bilateria. Yet, ctenophore features are more diverse and distinct, expressing up to twenty genes compared to six in vertebrates. Moreover, collagen IV is absent in unicellular sister-groups. Collectively, we conclude that collagen IV and its variant, spongin, are primordial components of the extracellular microenvironment, and as a component of BM, collagen IV enabled the assembly of a fundamental architectural unit for multicellular tissue genesis.
Keywords: Basement Membrane; Collagen IV; Ctenophora; developmental biology; epithelial cells; evolutionary biology; genomics; stem cells.
Conflict of interest statement
AR: Reviewing editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures

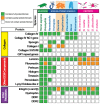

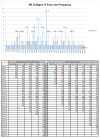

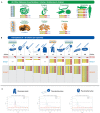




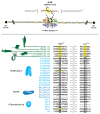




References
-
- Aouacheria A, Geourjon C, Aghajari N, Navratil V, Deléage G, Lethias C, Exposito JY. Insights into early extracellular matrix evolution: spongin short chain collagen-related proteins are homologous to basement membrane type IV collagens and form a novel family widely distributed in invertebrates. Molecular Biology and Evolution. 2006;23:2288–2302. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msl100. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhave G, Cummings CF, Vanacore RM, Kumagai-Cresse C, Ero-Tolliver IA, Rafi M, Kang JS, Pedchenko V, Fessler LI, Fessler JH, Hudson BG. Peroxidasin forms sulfilimine chemical bonds using hypohalous acids in tissue genesis. Nature Chemical Biology. 2012;8:784–790. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1038. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

