A pathway linking reward circuitry, impulsive sensation-seeking and risky decision-making in young adults: identifying neural markers for new interventions
- PMID: 28418404
- PMCID: PMC5416701
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2017.60
A pathway linking reward circuitry, impulsive sensation-seeking and risky decision-making in young adults: identifying neural markers for new interventions
Abstract
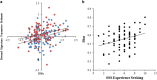
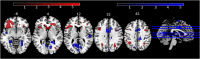
High trait impulsive sensation seeking (ISS) is common in 18-25-year olds, and is associated with risky decision-making and deleterious outcomes. We examined relationships among: activity in reward regions previously associated with ISS during an ISS-relevant context, uncertain reward expectancy (RE), using fMRI; ISS impulsivity and sensation-seeking subcomponents; and risky decision-making in 100, transdiagnostically recruited 18-25-year olds. ISS, anhedonia, anxiety, depression and mania were measured using self-report scales; clinician-administered scales also assessed the latter four. A post-scan risky decision-making task measured 'risky' (possible win/loss/mixed/neutral) fMRI-task versus 'sure thing' stimuli. 'Bias' reflected risky over safe choices. Uncertain RE-related activity in left ventrolateral prefrontal cortex and bilateral ventral striatum was positively associated with an ISS composite score, comprising impulsivity and sensation-seeking-fun-seeking subcomponents (ISSc; P⩽0.001). Bias positively associated with sensation seeking-experience seeking (ES; P=0.003). This relationship was moderated by ISSc (P=0.009): it was evident only in high ISSc individuals. Whole-brain analyses showed a positive relationship between: uncertain RE-related left ventrolateral prefrontal cortical activity and ISSc; uncertain RE-related visual attention and motor preparation neural network activity and ES; and uncertain RE-related dorsal anterior cingulate cortical activity and bias, specifically in high ISSc participants (all ps<0.05, peak-level, family-wise error corrected). We identify an indirect pathway linking greater levels of uncertain RE-related activity in reward, visual attention and motor networks with greater risky decision-making, via positive relationships with impulsivity, fun seeking and ES. These objective neural markers of high ISS can guide new treatment developments for young adults with high levels of this debilitating personality trait.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Evenden JL. Varieties of impulsivity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1999; 146: 348–361. - PubMed
-
- Zuckerman M. Chapter 31. Sensation seeking. In: Hoyle RH (ed). Handbook of Individual Differences in Social behavior. The Guildford Press: New York/London, pp 455–4652009.
-
- Whiteside SP, Lynam DR. The Five Factor Model and impulsivity: using a structural model of personality to understand impulsivity. Pers Indiv Differ 2001; 30: 669–689.
-
- Patton JH, Stanford MS, Barratt ES. Factor structure of the Barratt impulsiveness scale. J Clin Psychol 1995; 51: 768–774. - PubMed
-
- Carver CS, White TL. Behavioral inhibition, behavioral activation, and affective responses to impending reward and punishment: the BIS/BAS scales. J Pers Soc Psychol 1994; 67: 319–333.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

