Neurocognitive Trajectory of Boys Who Received a Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant at an Early Stage of Childhood Cerebral Adrenoleukodystrophy
- PMID: 28418523
- PMCID: PMC5540007
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.0013
Neurocognitive Trajectory of Boys Who Received a Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant at an Early Stage of Childhood Cerebral Adrenoleukodystrophy
Abstract
Importance: Untreated childhood cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy (cALD) is a fatal disease associated with progressive cerebral demyelination and rapid, devastating neurologic decline. The standard of care to enhance long-term survival and stabilize cerebral disease is a hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). Neurologic outcomes are better when HSCT occurs at an earlier stage of cALD, yet there is limited understanding of the neurocognitive trajectory of patients who undergo HSCT.
Objectives: To characterize neurocognitive outcomes of boys with cALD and early-stage cerebral disease who were treated with an allogeneic HSCT and to identify disease- and treatment-related factors associated with long-term functioning.
Design, setting, and participants: Baseline and follow-up neurocognitive test performance was analyzed for all boys with cALD who received an HSCT at the University of Minnesota between January 1, 1991, and October 20, 2014, and who had a pretransplant magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) severity score of less than 10 (scale range, 0-34; higher scores indicate greater severity).
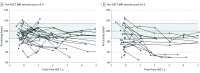
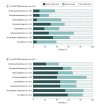
Main outcomes and measures: Longitudinal neurocognitive test performance in 4 domains (verbal comprehension, perceptual [visual] reasoning, working memory, and processing speed) were the primary outcome measures. Secondary analysis at the most recent evaluation also included measures of sustained attention, verbal memory, visual-motor integration, and fine motor function.
Results: Among the 62 boys in this study (mean [SD] age at transplant, 8.37 [2.80] years; range, 4-16 years), there was a significant association of pretransplant MRI severity and baseline verbal comprehension (r = -0.340; P = .008), perceptual reasoning (r = -0.419; P = .001), and processing speed (r = -0.285; P = .03) scores. Higher pretransplant MRI severity scores were also associated with a steeper decline in neurocognitive functioning during the 5-year follow-up period. Twenty-two of 33 patients (67%) with available long-term follow-up neurocognitive testing had severe impairment in at least 1 neurocognitive domain at the most recent evaluation.
Conclusions and relevance: Boys with cALD who have greater than minimal cerebral disease detected on MRI scans at the time of an HSCT are at risk for severe, persistent neurocognitive deficits. These findings motivate further exploration of methods of detecting cerebral disease prior to development of lesions observable on MRI scans, an endeavor that may be facilitated by newborn screening for adrenoleukodystrophy. These findings may serve a benchmark role in evaluating the efficacy of novel interventions for cALD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Decision Making in Adrenoleukodystrophy: When Is a Good Outcome Really a Good Outcome?JAMA Neurol. 2017 Jun 1;74(6):641-642. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.0095. JAMA Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28418445 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Potential Risks to Stable Long-term Outcome of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Children With Cerebral X-linked Adrenoleukodystrophy.JAMA Netw Open. 2018 Jul 6;1(3):e180769. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.0769. JAMA Netw Open. 2018. PMID: 30646031 Free PMC article.
-
Differential outcomes for frontal versus posterior demyelination in childhood cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021 Nov;44(6):1434-1440. doi: 10.1002/jimd.12435. Epub 2021 Sep 17. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2021. PMID: 34499753 Free PMC article.
-
Survival and Functional Outcomes in Boys with Cerebral Adrenoleukodystrophy with and without Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019 Mar;25(3):538-548. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2018.09.036. Epub 2018 Oct 4. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30292747
-
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Brain Pathol. 2010 Jul;20(4):857-62. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2010.00394.x. Brain Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20626747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hematopoietic stem cell therapy and ex vivo gene therapy for X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Handb Clin Neurol. 2024;202:265-278. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-90242-7.00018-3. Handb Clin Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39111913 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between APOE4 and biomarkers in cerebral adrenoleukodystrophy.Sci Rep. 2019 May 27;9(1):7858. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44140-3. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31133696 Free PMC article.
-
The Landscape of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant and Gene Therapy for X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy.Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019 Nov 25;21(12):61. doi: 10.1007/s11940-019-0605-y. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31768791 Review.
-
Multi-Omic Approach to Identify Phenotypic Modifiers Underlying Cerebral Demyelination in X-Linked Adrenoleukodystrophy.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Jun 25;8:520. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00520. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32671069 Free PMC article.
-
B cell depletion can be effective in multiple sclerosis but failed in a patient with advanced childhood cerebral X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2019 Aug 14;12:1756286419868133. doi: 10.1177/1756286419868133. eCollection 2019. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2019. PMID: 31452685 Free PMC article.
-
Bone marrow transplantation reverses metabolic alterations in multiple sulfatase deficiency: a case series.Commun Med (Lond). 2025 Jan 9;5(1):12. doi: 10.1038/s43856-024-00703-8. Commun Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39789203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bezman L, Moser AB, Raymond GV, et al. . Adrenoleukodystrophy: incidence, new mutation rate, and results of extended family screening. Ann Neurol. 2001;49(4):512-517. - PubMed
-
- Kaltsas G, Kanakis G, Moser H. Adrenal insufficiency due to X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy In: De Groot LJ, Chrousos G, Dungan K, et al. , eds. Endotext. South Dartmouth, MA: MDText.com, Inc; 2000.
-
- Shimozawa N, Honda A, Kajiwara N, et al. . X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: diagnostic and follow-up system in Japan. J Hum Genet. 2011;56(2):106-109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

