Towards Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Models of Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia
- PMID: 28418603
- PMCID: PMC5445232
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.12191
Towards Quantitative Systems Pharmacology Models of Chemotherapy-Induced Neutropenia
Abstract
Neutropenia is a serious toxic complication of chemotherapeutic treatment. For years, mathematical models have been developed to better predict hematological outcomes during chemotherapy in both the traditional pharmaceutical sciences and mathematical biology disciplines. An increasing number of quantitative systems pharmacology (QSP) models that combine systems approaches, physiology, and pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics have been successfully developed. Here, I detail the shift towards QSP efforts, emphasizing the importance of incorporating systems-level physiological considerations in pharmacometrics.
© 2017 The Authors CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Figures
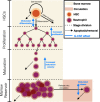

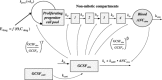
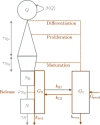
References
-
- Mantovani, A. , Cassatella, M.A. , Costantini, C. & Jaillon, S. Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 519–531 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Pillay, J. et al In vivo labeling with 2H2O reveals a human neutrophil lifespan of 5.4 days. Blood 116(4), 625–627 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

