Relationship of Trochlear Morphology and Patellofemoral Joint Alignment to Superolateral Hoffa Fat Pad Edema on MR Images in Individuals with or at Risk for Osteoarthritis of the Knee: The MOST Study
- PMID: 28418810
- PMCID: PMC5584646
- DOI: 10.1148/radiol.2017162342
Relationship of Trochlear Morphology and Patellofemoral Joint Alignment to Superolateral Hoffa Fat Pad Edema on MR Images in Individuals with or at Risk for Osteoarthritis of the Knee: The MOST Study
Abstract
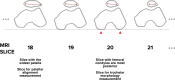
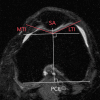
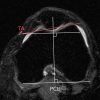
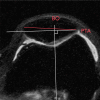
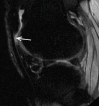
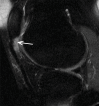
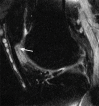
Purpose To determine the relationship of patellofemoral joint alignment and trochlear morphology to superolateral Hoffa fat pad (SHFP) edema on magnetic resonance (MR) images in older adults with or at risk for osteoarthritis of the knee. Materials and Methods Institutional review board approval and written informed consent were obtained from all subjects. The Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study is a prospective cohort study of older adults with or at risk for osteoarthritis of the knee. Subjects were recruited from Birmingham, Alabama, and Iowa City, Iowa. In this cross-sectional study, patellofemoral joint alignment (bisect offset, patellar tilt angle, and Insall-Salvati ratio), trochlear morphology (sulcus angle, lateral and medial trochlear inclination, and trochlear angle) and SHFP edema were assessed on MR images of the knee. Measures of alignment and morphology were divided into quartiles, and SHFP was determined to be present or absent. Separate logistic regression models were used to determine the relationship of each measure of alignment and morphology to the presence of SHFP edema, with adjustments for age, sex, and body mass index. Results SHFP edema was present in 152 (13.4%) of the 1134 knees that were included. When compared with knees with measurements in the lowest quartile, knees with measurements in the highest quartile for trochlear angle, bisect offset, and Insall-Salvati ratios were 1.6 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.0, 2.6), 2.3 (95% CI: 1.3, 4.0), and 8.9 (95% CI: 4.7, 16.9) times more likely to show SHFP edema, respectively. No relationship was found between other measures and SHFP edema. Conclusion A more anterior trochlear facet, a more laterally displaced patella, and knees with patella alta were significantly associated with SHFP edema on MR images in subjects with or at risk for osteoarthritis of the knee. © RSNA, 2017.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Superolateral Hoffa's fat pad (SHFP) oedema and patellar cartilage volume loss: quantitative analysis using longitudinal data from the Foundation for the National Institute of Health (FNIH) Osteoarthritis Biomarkers Consortium.Eur Radiol. 2018 Oct;28(10):4134-4145. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5334-1. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29651769
-
Superolateral Hoffa Fat Pad Edema and Patellofemoral Maltracking: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020 Sep;215(3):545-558. doi: 10.2214/AJR.19.22263. Epub 2020 Jun 6. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020. PMID: 32507017
-
Superolateral Hoffa fat pad edema in adolescent competitive alpine skiers: temporal evolution over 4 years and risk factors.Insights Imaging. 2024 Feb 16;15(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01633-8. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38365902 Free PMC article.
-
Superolateral Hoffa's fat pad oedema: Relationship with cartilage T2* value and patellofemoral maltracking.Eur J Radiol. 2019 Sep;118:122-129. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.07.012. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Eur J Radiol. 2019. PMID: 31439231
-
Osteoarthritic knees have a highly variable patellofemoral alignment: a systematic review.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021 Feb;29(2):483-490. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-05928-3. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2021. PMID: 32162047
Cited by
-
Using Dual-Orthogonal Fluoroscopy and CT to Assess the Relationship Between Knee Morphology and Patellar Kinematics in Patients With Patellofemoral Pain.Cureus. 2023 Aug 25;15(8):e44139. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44139. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37753041 Free PMC article.
-
Relation of Patellofemoral Joint Alignment, Morphology, and Radiographic Osteoarthritis to Frequent Anterior Knee Pain: Data from the Multicenter Osteoarthritis Study.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020 Aug;72(8):1066-1073. doi: 10.1002/acr.24004. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020. PMID: 31199605 Free PMC article.
-
Association of markers of patellofemoral maltracking to cartilage damage and bone marrow lesions on MRI: Data from the 2016 Olympic Games of Rio De Janeiro.Eur J Radiol Open. 2021 Oct 4;8:100381. doi: 10.1016/j.ejro.2021.100381. eCollection 2021. Eur J Radiol Open. 2021. PMID: 34660850 Free PMC article.
-
The association between patella alignment and morphology and knee osteoarthritis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Aug 27;19(1):509. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05001-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39192379 Free PMC article.
-
Superolateral Hoffa's fat pad (SHFP) oedema and patellar cartilage volume loss: quantitative analysis using longitudinal data from the Foundation for the National Institute of Health (FNIH) Osteoarthritis Biomarkers Consortium.Eur Radiol. 2018 Oct;28(10):4134-4145. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5334-1. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Eur Radiol. 2018. PMID: 29651769
References
-
- Roemer FW, Jarraya M, Felson DT, et al. . Magnetic resonance imaging of Hoffa’s fat pad and relevance for osteoarthritis research: a narrative review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2016;24(3):383–397. - PubMed
-
- Chung CB, Skaf A, Roger B, Campos J, Stump X, Resnick D. Patellar tendon-lateral femoral condyle friction syndrome: MR imaging in 42 patients. Skeletal Radiol 2001;30(12):694–697. - PubMed
-
- Campagna R, Pessis E, Biau DJ, et al. . Is superolateral Hoffa fat pad edema a consequence of impingement between lateral femoral condyle and patellar ligament? Radiology 2012;263(2):469–474. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

