High serum lactate dehydrogenase predicts an unfavorable outcome in Chinese elderly patients with multiple myeloma
- PMID: 28418851
- PMCID: PMC5564653
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16237
High serum lactate dehydrogenase predicts an unfavorable outcome in Chinese elderly patients with multiple myeloma
Abstract
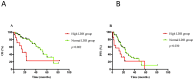
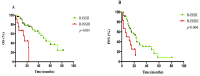
There is significant heterogeneity among multiple myeloma (MM) patients with the survival duration varying greatly from a few months to several years. This study retrospectively analyzed serum lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) in 105 cases of newly diagnosed elderly MM patients to investigate its value for outcome prediction. Serum LDH concentrations were evaluated prior to induction therapy. Prognostic analyses were carried out based on LDH levels and patients' other clinical data. We also applied the recently proposed Revised International Staging System (R-ISS) to 70 patients with the available data. Of all the patients, elevated serum LDH levels (≥271U/L) were observed in 13.3% (14 out of 105) patients at diagnosis. Compared with normal LDH group, high LDH group had significantly shorter overall survival (OS) (15.5 vs. 52.5 months, p = 0.002) and median progression free survival (PFS) (12.0 vs. 24 months, p = 0.030), as well as 2-year OS rate (20% vs. 81%, p < 0.001) and PFS rate (22% vs. 44%, p = 0.005). A multivariate analysis identified high LDH as a unique independent adverse prognostic parameter for both OS and PFS. In addition, there were significant differences between R-ISS II and R-ISS III patients in both median OS (52.5 vs. 15.5 months, p < 0.001) and PFS (23 vs. 7.5 months, p = 0.004). Furthermore, high LDH was a unique independent adverse indicator for overall response rate (ORR) and early death in elderly MM patients. These results identified LDH as an unfavorable prediction for the outcome of Chinese elderly patients with MM. R-ISS based on LDH is superior to ISS in prognostic assessment.
Keywords: LDH; R-ISS; multiple myeloma; outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High serum lactate dehydrogenase adds prognostic value to the international myeloma staging system even in the era of novel agents.Eur J Haematol. 2010 Aug;85(2):114-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.2010.01466.x. Epub 2010 May 6. Eur J Haematol. 2010. PMID: 20477863
-
LDH is an adverse prognostic factor independent of ISS in transplant-eligible myeloma patients receiving bortezomib-based induction regimens.Eur J Haematol. 2015 Apr;94(4):330-5. doi: 10.1111/ejh.12434. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Eur J Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25135740
-
Re-evaluation of prognostic markers including staging, serum free light chains or their ratio and serum lactate dehydrogenase in multiple myeloma patients receiving novel agents.Hematol Oncol. 2013 Jun;31(2):96-102. doi: 10.1002/hon.2026. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Hematol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 22961993
-
Staging systems and prognostic factors as a guide to therapeutic decisions in multiple myeloma.Semin Hematol. 2009 Apr;46(2):110-7. doi: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2009.02.004. Semin Hematol. 2009. PMID: 19389494 Review.
-
Circulating plasma cells as a predictive biomarker in Multiple myeloma: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2338604. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2338604. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 38599340 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Survival Outcomes of Newly Diagnosed Multiple Myeloma at a Tertiary Care Center in North India (IMAGe: 001A Study).JCO Glob Oncol. 2021 May;7:704-715. doi: 10.1200/GO.20.00625. JCO Glob Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33999651 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of the Controlling Nutritional Status score in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Sep 15;16(9):4788-4795. doi: 10.62347/FYJJ5585. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39398615 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin as adjuvant therapy to improve remission in myeloma patients: A pilot randomized clinical trial.Caspian J Intern Med. 2022 Spring;13(2):375-384. doi: 10.22088/cjim.13.2.9. Caspian J Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35919637 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic changes underlying drug resistance in the multiple myeloma tumor microenvironment.Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 6;13:1155621. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1155621. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37091139 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-125b as a valuable predictive marker for outcome after autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.BMC Cancer. 2023 Mar 3;23(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10665-0. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36869286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palumbo A, Anderson K. Multiple myeloma. The New England journal of medicine. 2011;364:1046–1060. - PubMed
-
- Gkotzamanidou M, Kastritis E, Gavriatopoulou MRMMM, Nikitas N, Gika D, Mparmparousi D, Matsouka C, Terpos E, Dimopoulos MA. Increased serum lactate dehydrongenase should be included among the variables that define very-high-risk multiple myeloma. Clinical lymphoma myeloma and leukemia. 2011;11:409–413. - PubMed
-
- Dawson SI. Long-term risk of malignant neoplasm associated with gestational glucose intolerance. Cancer. 2004;100:149–155. - PubMed
-
- Terpos E, Katodritou E, Roussou M, Pouli A, Michalis E, Delimpasi S, Parharidou A, Kartasis Z, Zomas A, Symeonidis A, Viniou NA, Anagnostopoulos N, Economopoulos T, et al. High serum lactate dehydrogenase adds prognostic value to the international myeloma staging system even in the era of novel agents. European journal of haematology. 2010;85:114–119. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical