BH3-mimetics and BET-inhibitors elicit enhanced lethality in malignant glioma
- PMID: 28418907
- PMCID: PMC5444687
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16365
BH3-mimetics and BET-inhibitors elicit enhanced lethality in malignant glioma
Abstract
Drug combination therapies remain pivotal for the treatment of heterogeneous malignancies, such as glioblastomas. Here, we show a novel lethal interaction between Bcl-xL and c-myc inhibition accomplished by bromodomain protein inhibitors. Established, patient-derived xenograft and stem cell-like glioma cells were treated with the novel bromodomain protein inhibitors, JQ1 and OTX015, along with BH3-mimetics, ABT263 or Obatoclax. Synergy was assessed by calculation of CI values. Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) were used for gene silencing and mechanistic studies. In vivo experiments were performed in a glioblastoma xenograft model. Single treatments with JQ1 and OTX015 had only moderate effects on the reduction of cellular viability. However, the combination treatment of BH3-mimetics along with JQ1 or OTX015 resulted in a highly synergistic reduction of cellular viability in a broad range of different model systems of malignant glioma. Similarly, knockdown of c-myc sensitized glioma cells for ABT263 mediated cell death. The enhanced loss of cellular viability in the combination treatment was mediated by activation of apoptosis with dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential and caspase cleavage. The combination treatment led to a modulation of anti- and pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members with an increase in pro-apoptotic Noxa mediated by ATF4. Small interfering RNA mediated knockdown of Bak and Noxa protected glioma cells from ABT263/JQ1 mediated apoptosis. Finally, the combination treatment of ABT263 and OTX015 resulted in a regression of tumors and a significantly smaller tumor size as compared to single or vehicle treated tumors. Thus, these results warrant clinical testing for the drug combination of BH3-mimetics along with bromodain protein inhibitors.
Keywords: BH3-mimetics; Bcl-xL; apoptosis; brain cancer; c-myc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures

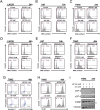
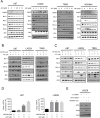
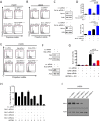
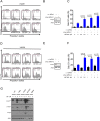

Comment in
-
BET-inhibitors as sensitizers for BH3-mimetics.Aging (Albany NY). 2017 Jun 26;9(6):1475-1476. doi: 10.18632/aging.101259. Aging (Albany NY). 2017. PMID: 28657545 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Wei W, Shin YS, Xue M, Matsutani T, Masui K, Yang H, Ikegami S, Gu Y, Herrmann K, Johnson D, Ding X, Hwang K, Kim J, et al. Single-Cell Phosphoproteomics Resolves Adaptive Signaling Dynamics and Informs Targeted Combination Therapy in Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:563–73. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Toyoshima M, Howie HL, Imakura M, Walsh RM, Annis JE, Chang AN, Frazier J, Chau BN, Loboda A, Linsley PS, Cleary MA, Park JR, Grandori C. Functional genomics identifies therapeutic targets for MYC-driven cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109:9545–50. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1121119109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

