Leukotriene A4 Hydrolase Genotype and HIV Infection Influence Intracerebral Inflammation and Survival From Tuberculous Meningitis
- PMID: 28419368
- PMCID: PMC5426373
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jix050
Leukotriene A4 Hydrolase Genotype and HIV Infection Influence Intracerebral Inflammation and Survival From Tuberculous Meningitis
Abstract
Background: Tuberculous meningitis (TBM) is the most devastating form of tuberculosis, yet very little is known about the pathophysiology. We hypothesized that the genotype of leukotriene A4 hydrolase (encoded by LTA4H), which determines inflammatory eicosanoid expression, influences intracerebral inflammation, and predicts survival from TBM.
Methods: We characterized the pretreatment clinical and intracerebral inflammatory phenotype and 9-month survival of 764 adults with TBM. All were genotyped for single-nucleotide polymorphism rs17525495, and inflammatory phenotype was defined by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leukocyte and cytokine concentrations.
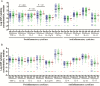
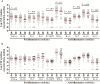
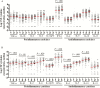
Results: LTA4H genotype predicted survival of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-uninfected patients, with TT-genotype patients significantly more likely to survive TBM than CC-genotype patients, according to Cox regression analysis (univariate P = .040 and multivariable P = .037). HIV-uninfected, TT-genotype patients had high CSF proinflammatory cytokine concentrations, with intermediate and lower concentrations in those with CT and CC genotypes. Increased CSF cytokine concentrations correlated with more-severe disease, but patients with low CSF leukocytes and cytokine concentrations were more likely to die from TBM. HIV infection independently predicted death due to TBM (hazard ratio, 3.94; 95% confidence interval, 2.79-5.56) and was associated with globally increased CSF cytokine concentrations, independent of LTA4H genotype.
Conclusions: LTA4H genotype and HIV infection influence pretreatment inflammatory phenotype and survival from TBM. LTA4H genotype may predict adjunctive corticosteroid responsiveness in HIV-uninfected individuals.
Keywords: Leukotriene A4 hydrolase genotype; cytokines; inflammatory response; survival.; tuberculous meningitis.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures


Comment in
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Leukotriene B4 and Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor II Levels and Treatment Outcome in Tuberculous Meningitis.J Infect Dis. 2017 Aug 1;216(3):392-394. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix317. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28859433 No abstract available.
-
Informative, large cohorts of meningeal tuberculosis.Indian J Tuberc. 2017 Oct;64(4):241-242. doi: 10.1016/j.ijtb.2017.07.001. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Indian J Tuberc. 2017. PMID: 28941845 No abstract available.
References
-
- Thwaites GE, van Toorn R, Schoeman J. Tuberculous meningitis: more questions, still too few answers. Lancet Neurol 2013; 12:999–1010. - PubMed
-
- Dastur DK, Manghani DK, Udani PM. Pathology and pathogenetic mechanisms in neurotuberculosis. Radiol Clin North Am 1995; 33:733–52. - PubMed
-
- Shane SJ, Riley C. Tuberculous meningitis: combined therapy with cortisone and antimicrobial agents. N Engl J Med 1953; 249:829–34. - PubMed
-
- Prasad K, Singh MB. Corticosteroids for managing tuberculous meningitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2008:CD002244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

