The life sulfuric: microbial ecology of sulfur cycling in marine sediments
- PMID: 28419734
- PMCID: PMC5573963
- DOI: 10.1111/1758-2229.12538
The life sulfuric: microbial ecology of sulfur cycling in marine sediments
Abstract
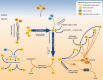
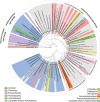
Almost the entire seafloor is covered with sediments that can be more than 10 000 m thick and represent a vast microbial ecosystem that is a major component of Earth's element and energy cycles. Notably, a significant proportion of microbial life in marine sediments can exploit energy conserved during transformations of sulfur compounds among different redox states. Sulfur cycling, which is primarily driven by sulfate reduction, is tightly interwoven with other important element cycles (carbon, nitrogen, iron, manganese) and therefore has profound implications for both cellular- and ecosystem-level processes. Sulfur-transforming microorganisms have evolved diverse genetic, metabolic, and in some cases, peculiar phenotypic features to fill an array of ecological niches in marine sediments. Here, we review recent and selected findings on the microbial guilds that are involved in the transformation of different sulfur compounds in marine sediments and emphasise how these are interlinked and have a major influence on ecology and biogeochemistry in the seafloor. Extraordinary discoveries have increased our knowledge on microbial sulfur cycling, mainly in sulfate-rich surface sediments, yet many questions remain regarding how sulfur redox processes may sustain the deep-subsurface biosphere and the impact of organic sulfur compounds on the marine sulfur cycle.
© 2017 The Authors. Environmental Microbiology published by Society for Applied Microbiology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Badziong, W. , and Thauer, R.K. (1978) Growth yields and growth rates of Desulfovibrio vulgaris (Marburg) growing on hydrogen plus sulfate and hydrogen plus thiosulfate as the sole energy sources. Arch Microbiol 117: 209–214. - PubMed
-
- Bak, F. , and Cypionka, H. (1987) A novel type of energy‐metabolism involving fermentation of inorganic sulfur‐compounds. Nature 326: 891–892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

