Plantago asiatica L. Ameliorates Puromycin Aminonucleoside-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome by Suppressing Inflammation and Apoptosis
- PMID: 28420111
- PMCID: PMC5409725
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9040386
Plantago asiatica L. Ameliorates Puromycin Aminonucleoside-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome by Suppressing Inflammation and Apoptosis
Abstract
Objective: Nephrotic syndrome, a kidney disease with a variety of causes, is mainly characterized by heavy proteinuria, hypoproteinemia, and ascites. This study was designed to evaluate the underlying mechanism of action of Plantago asiatica L. (PAL) in treating nephrotic syndrome induced by puromycin aminonucleoside.
Methods: PAL has been used in Asia as a traditional medicine and dietary health supplement. Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were intravenously injected with puromycin aminonucleoside (75 mg/kg/day), then treated with either Losartan (30 mg/kg/day) or PAL (200 mg/kg/day) by oral gavage for seven days.
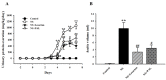
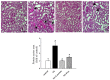
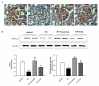
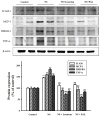
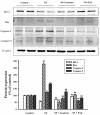
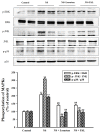
Results: PAL significantly decreased ascites, proteinuria level, and plasma lipid parameters. In addition, treatment with PAL attenuated histological damage and hypoalbuminemia. Treatment with PAL also restored podocin expression and reduced inflammation markers such as intracellular adhesion molecules (ICAM-1), monocyte chemotactic protein-1 (MCP-1), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and high-mobility group box-1 (HMGB1). Lower expression levels of the apoptosis markers Bax, caspase-3 and capase-9 were documented in SD rats receiving PAL. PAL also significantly decreased the phosphorylation levels of MAPKs such as ERK, JNK and p38.
Conclusion: As a multifunctional agent, PAL has a renoprotective effect in nephrotic syndrome rat models. The anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic properties, along with reductions in hyperlipidemia and ascites, represent important therapeutic effects. These results indicate that Plantago asiatica is likely to be a promising agent in the treatment of nephrotic syndrome.
Keywords: apoptosis; ascites; inflammation; nephrotic syndrome; plantago asiatica.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bulucu F., Vural A., Aydin A., Sayal A. Oxidative stress status in adults with nephrotic syndrome. Clin. Nephrol. 2000;53:169–173. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

