The Modeling and Simulation of the Galvanic Coupling Intra-Body Communication via Handshake Channel
- PMID: 28420119
- PMCID: PMC5424740
- DOI: 10.3390/s17040863
The Modeling and Simulation of the Galvanic Coupling Intra-Body Communication via Handshake Channel
Abstract
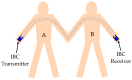
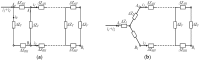
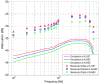
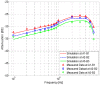
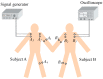
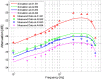
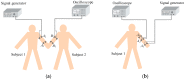
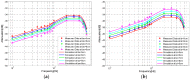
Intra-body communication (IBC) is a technology using the conductive properties of the body to transmit signal, and information interaction by handshake is regarded as one of the important applications of IBC. In this paper, a method for modeling the galvanic coupling intra-body communication via handshake channel is proposed, while the corresponding parameters are discussed. Meanwhile, the mathematical model of this kind of IBC is developed. Finally, the validity of the developed model has been verified by measurements. Moreover, its characteristics are discussed and compared with that of the IBC via single body channel. Our results indicate that the proposed method will lay a foundation for the theoretical analysis and application of the IBC via handshake channel.
Keywords: Information interaction; galvanic coupling; intra-body communication; transfer function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
A finite-element simulation of galvanic coupling intra-body communication based on the whole human body.Sensors (Basel). 2012 Oct 9;12(10):13567-82. doi: 10.3390/s121013567. Sensors (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23202010 Free PMC article.
-
Comparable Investigation of Characteristics for Implant Intra-Body Communication Based on Galvanic and Capacitive Coupling.IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2019 Dec;13(6):1747-1758. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2019.2940827. Epub 2019 Sep 11. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst. 2019. PMID: 31514153
-
Modeling for intra-body communication with bone effect.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009;2009:693-6. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5332703. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2009. PMID: 19963722
-
A survey on intrabody communications for body area network applications.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2013 Aug;60(8):2067-79. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2013.2254714. Epub 2013 Mar 27. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2013. PMID: 23542945 Review.
-
To core, or not to core: the impact of coring on tree health and a best-practice framework for collecting dendrochronological information from living trees.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2016 Nov;91(4):899-924. doi: 10.1111/brv.12200. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2016. PMID: 26105027 Review.
Cited by
-
New Contact Sensorization Smart System for IoT e-Health Applications Based on IBC IEEE 802.15.6 Communications.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Dec 11;20(24):7097. doi: 10.3390/s20247097. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33322315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zimmerman T.G. Personal Area Networks (PAN): Near-Field Intra-Body Communication. Massachusetts Institute of Technology; Cambridge, MA, USA: 1995.
-
- Gravina R., Alinia P., Ghasemzadeh H., Fortino G. Multi-sensor fusion in body sensor networks: State-of-the-art and research challenges. Inf. Fusion. 2017;35:68–80. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.09.005. - DOI
-
- Fortino G., Giannantonio R., Gravina R., Kuryloski P., Jafari R. Enabling Effective Programming and Flexible Management of Efficient Body Sensor Network Applications. IEEE Trans. Hum. Mach. Syst. 2013;43:115–133. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2012.2215852. - DOI
-
- Iyengar S., Bonda F.T., Gravina R., Guerrieri A., Fortino G., Sangiovanni-Vincentelli A. A framework for creating healthcare monitoring applications using wireless body sensor networks; Proceedings of the ICST 3rd International Conference Body Area Networks; Tempe, AZ, USA. 13–17 March 2008.
-
- Shinagawa M., Fu M., Ochiai K., Kyuragi H. A near-field-sensing transceiver for intrabody communication based on the electrooptic effect. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2004;6:1533–1538. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2004.834064. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

