Interplay between Oxidative Stress and Nutrient Sensing Signaling in the Developmental Origins of Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 28420139
- PMCID: PMC5412425
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18040841
Interplay between Oxidative Stress and Nutrient Sensing Signaling in the Developmental Origins of Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
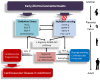
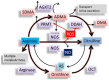
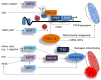
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) presents a global health burden, despite recent advances in management. CVD can originate from early life by so-called "developmental origins of health and disease" (DOHaD). Epidemiological and experimental evidence supports that early-life insults can induce programming of later CVD. Underlying the DOHaD concept, early intervention may offset programming process to prevent the development of CVD, namely reprogramming. Oxidative stress and nutrient sensing signals have been considered to be major mechanisms of cardiovascular programming, while the interplay between these two mechanisms have not been examined in detail. This review summarizes current evidence that supports the link between oxidative stress and nutrient sensing signaling to cardiovascular programming, with an emphasis on the l-arginine-asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA)-nitric oxide (NO) pathway. This review provides an overview of evidence from human studies supporting fetal programming of CVD, insight from animal models of cardiovascular programming and oxidative stress, impact of the l-arginine-ADMA-NO pathway in cardiovascular programming, the crosstalk between l-arginine metabolism and nutrient sensing signals, and application of reprogramming interventions to prevent the programming of CVD. A greater understanding of the mechanisms underlying cardiovascular programming is essential to developing early reprogramming interventions to combat the globally growing epidemic of CVD.
Keywords: arginine; asymmetric dimethylarginine; cardiovascular disease; developmental origins of health and disease (DOHaD); hypertension; nitric oxide; nutrient sensing; oxidative stress; phytonutrient; symmetric dimethylarginine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting on Asymmetric Dimethylarginine-Related Nitric Oxide-Reactive Oxygen Species Imbalance to Reprogram the Development of Hypertension.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Dec 2;17(12):2020. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122020. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27918455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Nitric Oxide Production in the Developmental Programming of Hypertension and Kidney Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 5;20(3):681. doi: 10.3390/ijms20030681. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30764498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventing Developmental Origins of Cardiovascular Disease: Hydrogen Sulfide as a Potential Target?Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 5;10(2):247. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020247. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33562763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental Origins of Chronic Kidney Disease: Should We Focus on Early Life?Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 11;18(2):381. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020381. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28208659 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developmental Programming of Adult Disease: Reprogramming by Melatonin?Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Feb 16;18(2):426. doi: 10.3390/ijms18020426. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28212315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Acupuncture on Oxidative Stress Amelioration via Nrf2/ARE-Related Pathways in Alzheimer and Parkinson Diseases.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Apr 26;2021:6624976. doi: 10.1155/2021/6624976. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 33995547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress-Induced Hypertension of Developmental Origins: Preventive Aspects of Antioxidant Therapy.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 7;11(3):511. doi: 10.3390/antiox11030511. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early-Life Programming and Reprogramming of Adult Kidney Disease and Hypertension: The Interplay between Maternal Nutrition and Oxidative Stress.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 18;21(10):3572. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103572. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32443635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect and mechanism of acupuncture on Alzheimer's disease: A review.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Mar 3;15:1035376. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1035376. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36936498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adverse Impact of Environmental Chemicals on Developmental Origins of Kidney Disease and Hypertension.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 14;12:745716. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.745716. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34721300 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

