Overexpression of S-Adenosyl-l-Methionine Synthetase 2 from Sugar Beet M14 Increased Arabidopsis Tolerance to Salt and Oxidative Stress
- PMID: 28420190
- PMCID: PMC5412431
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18040847
Overexpression of S-Adenosyl-l-Methionine Synthetase 2 from Sugar Beet M14 Increased Arabidopsis Tolerance to Salt and Oxidative Stress
Abstract
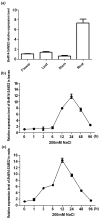
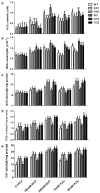
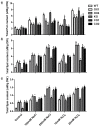
The sugar beet monosomic addition line M14 is a unique germplasm that contains genetic materials from Beta vulgaris L. and Beta corolliflora Zoss, and shows tolerance to salt stress. Our study focuses on exploring the molecular mechanism of the salt tolerance of the sugar beet M14. In order to identify differentially expressed genes in M14 under salt stress, a subtractive cDNA library was generated by suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH). A total of 36 unique sequences were identified in the library and their putative functions were analyzed. One of the genes, S-adenosylmethionine synthetase (SAMS), is the key enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), a precursor of polyamines. To determine the potential role of SAMS in salt tolerance, we isolated BvM14-SAMS2 from the salt-tolerant sugar beet M14. The expression of BvM14-SAMS2 in leaves and roots was greatly induced by salt stress. Overexpression of BvM14-SAMS2 in Arabidopsis resulted in enhanced salt and H₂O₂ tolerance. Furthermore, we obtained a knock-down T-DNA insertion mutant of AtSAMS3, which shares the highest homology with BvM14-SAMS2. Interestingly, the mutant atsam3 showed sensitivity to salt and H₂O₂ stress. We also found that the antioxidant system and polyamine metabolism play an important role in salt and H₂O₂ tolerance in the BvM14-SAMS2-overexpressed plants. To our knowledge, the function of the sugar beet SAMS has not been reported before. Our results have provided new insights into SAMS functions in sugar beet.
Keywords: ">l-methionine synthetase; S-adenosyl-; antioxidant system; polyamine; salt stress; sugar beet M14.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Turan M.A., Elkarim A.H.A., Taban N., Taban S. Effect of salt stress on growth, stomatal resistance, proline and chlorophyll concentrations on maize plant. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2009;4:893–897.
-
- Barkla B.J., Castellanos-Cervantes T., de León J.L., Matros A., Mock H.P., Perez-Alfocea F., Salekdeh G.H., Witzel K., Zörb C. Elucidation of salt stress defense and tolerance mechanisms of crop plants using proteomics—Current achievements and perspectives. Proteomics. 2013;13:1885–1900. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201200399. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

