A Phonocardiographic-Based Fiber-Optic Sensor and Adaptive Filtering System for Noninvasive Continuous Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring
- PMID: 28420215
- PMCID: PMC5426540
- DOI: 10.3390/s17040890
A Phonocardiographic-Based Fiber-Optic Sensor and Adaptive Filtering System for Noninvasive Continuous Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring
Abstract
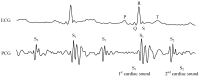
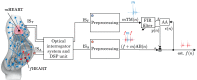
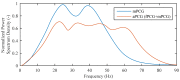
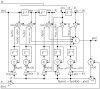
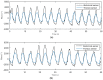
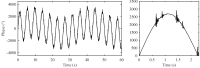
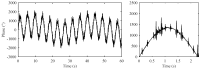
This paper focuses on the design, realization, and verification of a novel phonocardiographic- based fiber-optic sensor and adaptive signal processing system for noninvasive continuous fetal heart rate (fHR) monitoring. Our proposed system utilizes two Mach-Zehnder interferometeric sensors. Based on the analysis of real measurement data, we developed a simplified dynamic model for the generation and distribution of heart sounds throughout the human body. Building on this signal model, we then designed, implemented, and verified our adaptive signal processing system by implementing two stochastic gradient-based algorithms: the Least Mean Square Algorithm (LMS), and the Normalized Least Mean Square (NLMS) Algorithm. With this system we were able to extract the fHR information from high quality fetal phonocardiograms (fPCGs), filtered from abdominal maternal phonocardiograms (mPCGs) by performing fPCG signal peak detection. Common signal processing methods such as linear filtering, signal subtraction, and others could not be used for this purpose as fPCG and mPCG signals share overlapping frequency spectra. The performance of the adaptive system was evaluated by using both qualitative (gynecological studies) and quantitative measures such as: Signal-to-Noise Ratio-SNR, Root Mean Square Error-RMSE, Sensitivity-S+, and Positive Predictive Value-PPV.
Keywords: EMI-free; Least Mean Squares (LMS) algorithm; Normalized Least Mean Square (NLMS) algorithm; adaptive system; fetal heart rate (fHR); fetal heart sounds (fHS); fetal phonocardiography (fPCG); interferometer; maternal heart rate (mHR); maternal heart sounds (mHS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
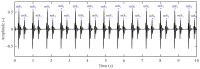
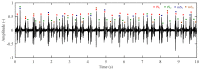
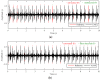
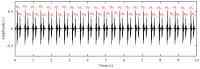
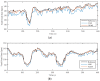
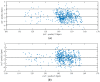
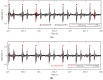
References
-
- Gabbe S.G., Niebyl J.R., Galan H.L., Jauniaux E.R.M., Simpson J.L., Driscoll D.A. Obstetrics: Normal and Problem Pregnancies. Elsevier Health Sciences; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2012.
-
- Oats J., Abraham S. Llewellyn-Jones Fundamentals of Obstetrics and Gynaecology. Elsevier Health Sciences; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2016.
-
- Hacker N.F., Gambone J.C., Hobel C.J. Hacker & Moore’s Essentials of Obstetrics and Gynecology. Elsevier Health Sciences; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2015.
-
- Alferic Z., Devane D., Gyte G.M. Continuous Cardiotocography (CTG) as a form of Electronic Fetal Monitoring (EFM) for Fetal Assessment during Labour. The Cochrane Library; New York, NY, USA: 2013. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

