Prognostic significance of TRAIL-R3 and CCR-2 expression in tumor epithelial cells of patients with early breast cancer
- PMID: 28420351
- PMCID: PMC5395831
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3259-8
Prognostic significance of TRAIL-R3 and CCR-2 expression in tumor epithelial cells of patients with early breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Tumor epithelial cells (TEpCs) and spindle-shaped stromal cells, not associated with the vasculature, of patients with early breast cancer express osteoprotegerin (OPG), tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B ligand, stromal cell derived factor-1, interleukin-6, macrophage colony stimulating factor, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand-2 (CCL-2) and their receptors at significantly higher levels compared with non-neoplastic breast tissues. We evaluated the clinicopathological significance of these ligands and receptors in TEpC and spindle-shaped stromal cells, not associated with the vasculature, to determine their impact on prognosis of patients with early-stage breast cancer.
Methods: We conducted immunohistochemical analyses of protein expression in primary tumors of patients with early breast cancer and analyzed their association with standard prognostic parameters and clinical outcomes, including local relapse, metastatic recurrence, disease-free survival (DFS), metastasis-free survival (MFS), and overall survival (OS).
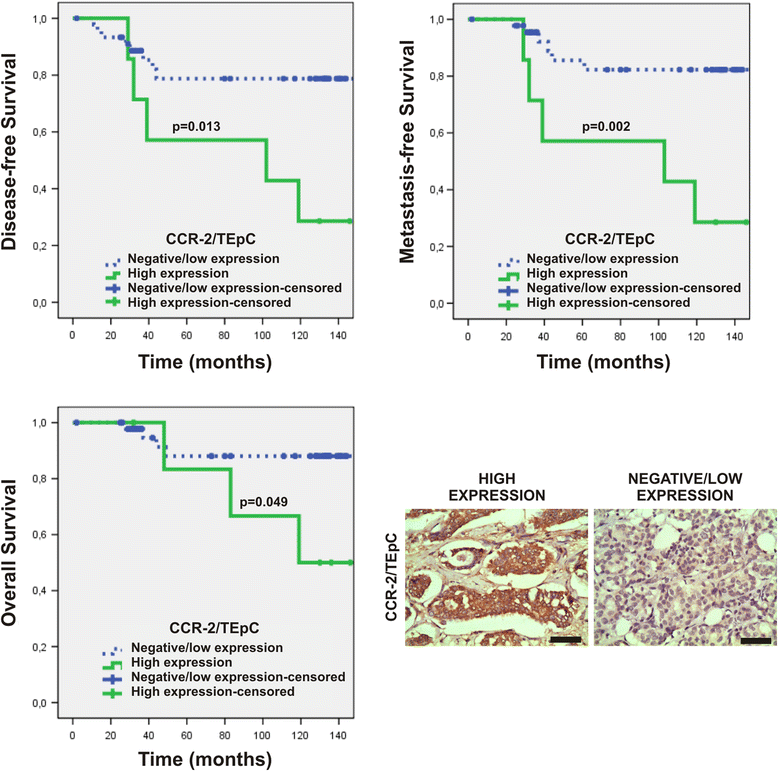
Results: Elevated levels of TRAIL-R3 and chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 2 (CCR-2) in TEpCs and OPG and CCL-2 in stromal cells were significantly associated with a higher risk of metastasis (p = 0.032, p = 0.003, p = 0.038, and p = 0.049; respectively). Moreover, high expression of TRAIL-R3 and CCR-2 in TEpCs was associated with shorter DFS, MFS, and OS. High TRAIL-R3 expression in TEpCs was an independent prognostic factor for DFS and OS, and high CCR-2 expression in these cells was an independent prognostic factor for MFS.
Conclusions: High levels of TRAIL-R3 and CCR-2 expression in TEpCs identified patients with early breast cancer with poor outcomes.
Keywords: CCR-2; Early breast cancer; Spindle-shaped stromal cells; TRAIL-R3; Tumor epithelial cells.
Figures


References
-
- Bhatia P, Sanders MM, Hansen MF. Expression of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB is inversely correlated with metastatic phenotype in breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(1):162–165. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

