Characterization of a novel aspartyl protease inhibitor from Haemonchus contortus
- PMID: 28420411
- PMCID: PMC5395858
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-017-2137-1
Characterization of a novel aspartyl protease inhibitor from Haemonchus contortus
Abstract
Background: Aspartyl protease inhibitor (API) was thought to protect intestinal parasitic nematodes from their hostile proteolytic environment. Studies on Ostertagia ostertagi, Ascaris suum and Brugia malayi indicated that aspins might play roles in nematode infection. In a recent study, proteins differentially expressed between free-living third-stage larvae (L3) and activated L3 (xL3) of Haemonchus contortus were identified by 2D-DIGE. API was found downregulated in xL3 when compared with L3. However, there was no report about the functions of H. contortus API in the parasite-host interaction. In this study, the gene encoding API from H. contortus was cloned, expressed, and part of its biological characteristics were studied.
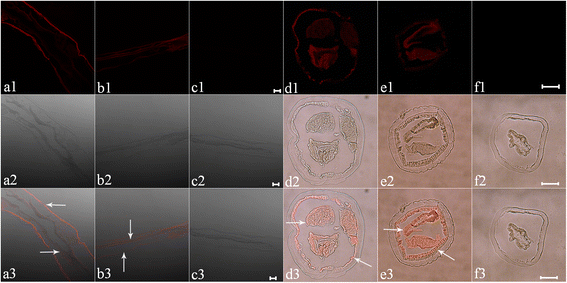
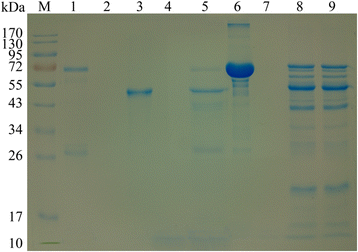
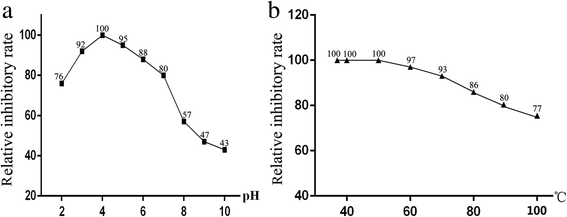
Results: A DNA fragment of 681 bp was amplified by RT-PCR. Ninety one percent of the amino acid sequence was similar with that for aspin from O. ostertagi. The recombinant API protein was fusion-expressed with a molecular weight of 48 × 103. Results of Western blot showed that the recombinant API could be recognized by serum from goat infected with H. contortus. It was found that API was localized exclusively in the subcutaneous tissue and epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract in adult H. contortus. qRT-PCR suggested that the API gene was differentially transcribed in different life-cycle stages, with the lowest level in female adults and the highest in free-living L3 larvae. Enzyme inhibition assay indicated that the recombinant API can inhibit the activity of pepsin significantly, and the optimal reaction pH and temperature were 4.0 and 37-50 °C respectively. In vitro study showed that the recombinant API could induce goat PBMCs to express IFN-γ, IL-4 and IL-10.
Conclusions: A new aspartyl protease inhibitor was cloned from H. contortus and its characteristics were studied for the first time. The results indicate that API may regulate the immune response of the host and play roles in the infection.
Keywords: Aspartyl protease inhibitor; Differential expression; Haemonchus contortus; Induction of cytokines; Inhibitory activity; Localization.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Cloning and characterisation of an aspartyl protease inhibitor (API-1) from Ancylostoma hookworms.Int J Parasitol. 2005 Mar;35(3):303-13. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2004.11.014. Epub 2005 Jan 8. Int J Parasitol. 2005. PMID: 15722082
-
Characterization of a secreted cystatin of the parasitic nematode Haemonchus contortus and its immune-modulatory effect on goat monocytes.Parasit Vectors. 2017 Sep 18;10(1):425. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2368-1. Parasit Vectors. 2017. PMID: 28923082 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel methyltransferase-type 12 protein from Haemonchus contortus and its effects on functions of goat PBMCs.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Mar 30;13(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04028-y. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32228657 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for exploring molecular developmental processes in Haemonchus contortus.Int J Parasitol. 2006 Jul;36(8):859-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2006.04.007. Epub 2006 May 17. Int J Parasitol. 2006. PMID: 16759659 Review.
-
The Pathophysiology, Ecology and Epidemiology of Haemonchus contortus Infection in Small Ruminants.Adv Parasitol. 2016;93:95-143. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2016.02.022. Epub 2016 May 10. Adv Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 27238004 Review.
Cited by
-
In vitro characterization of Haemonchus contortus trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase and its immunomodulatory effects on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs).Parasit Vectors. 2021 Dec 20;14(1):611. doi: 10.1186/s13071-021-05115-4. Parasit Vectors. 2021. PMID: 34930417 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of Haemonchus contortus Proteases and Protease Inhibitors Using Advanced Informatics Provides Insights into Parasite Biology and Host-Parasite Interactions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 1;24(15):12320. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512320. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569696 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional responses to in vitro macrocyclic lactone exposure in Toxocara canis larvae using RNA-seq.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 20:2024.12.20.629602. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.20.629602. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39763735 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Insights into the Role of Tick Salivary Protease Inhibitors during Ectoparasite-Host Crosstalk.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 17;22(2):892. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020892. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33477394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the immunomodulatory properties of Haemonchus contortus adhesion regulating molecule 1 interacting with goat T cells.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Aug 18;13(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04297-7. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32811556 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

