Excitatory neurons sculpt GABAergic neuronal connectivity in the C. elegans motor circuit
- PMID: 28420711
- PMCID: PMC5450832
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.141911
Excitatory neurons sculpt GABAergic neuronal connectivity in the C. elegans motor circuit
Abstract
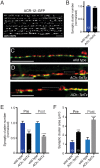
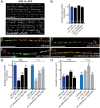
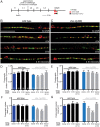
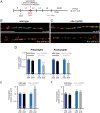
Establishing and maintaining the appropriate number of GABA synapses is key for balancing excitation and inhibition in the nervous system, though we have only a limited understanding of the mechanisms controlling GABA circuit connectivity. Here, we show that disrupting cholinergic innervation of GABAergic neurons in the C. elegans motor circuit alters GABAergic neuron synaptic connectivity. These changes are accompanied by reduced frequency and increased amplitude of GABAergic synaptic events. Acute genetic disruption in early development, during the integration of post-embryonic-born GABAergic neurons into the circuit, produces irreversible effects on GABAergic synaptic connectivity that mimic those produced by chronic manipulations. In contrast, acute genetic disruption of cholinergic signaling in the adult circuit does not reproduce these effects. Our findings reveal that GABAergic signaling is regulated by cholinergic neuronal activity, probably through distinct mechanisms in the developing and mature nervous system.
Keywords: E/I balance; GABA synapse; Neural circuit; Neural development.
© 2017. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Anaphase-Promoting Complex (APC) ubiquitin ligase regulates GABA transmission at the C. elegans neuromuscular junction.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2014 Jan;58:62-75. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 7. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24321454 Free PMC article.
-
Neurexin directs partner-specific synaptic connectivity in C. elegans.Elife. 2018 Jul 24;7:e35692. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35692. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30039797 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans Punctin specifies cholinergic versus GABAergic identity of postsynaptic domains.Nature. 2014 Jul 24;511(7510):466-70. doi: 10.1038/nature13313. Epub 2014 Jun 1. Nature. 2014. PMID: 24896188
-
C. elegans Locomotion: Finding Balance in Imbalance.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1112:185-196. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-3065-0_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30637699 Review.
-
Refining the roles of GABAergic signaling during neural circuit formation.Trends Neurosci. 2007 Aug;30(8):382-9. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2007.06.002. Epub 2007 Jun 27. Trends Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17590449 Review.
Cited by
-
Repression of an activity-dependent autocrine insulin signal is required for sensory neuron development in C. elegans.Development. 2019 Nov 19;146(22):dev182873. doi: 10.1242/dev.182873. Development. 2019. PMID: 31628111 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Directing Spine Outgrowth and Synaptic Partner Selection in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Exp Neurosci. 2018 Dec 2;12:1179069518816088. doi: 10.1177/1179069518816088. eCollection 2018. J Exp Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30546264 Free PMC article.
-
Building stereotypic connectivity: mechanistic insights into structural plasticity from C. elegans.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018 Feb;48:97-105. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2017.11.005. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 29182952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gain-of-function mutations in the UNC-2/CaV2α channel lead to excitation-dominant synaptic transmission in Caenorhabditis elegans.Elife. 2019 Aug 5;8:e45905. doi: 10.7554/eLife.45905. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31364988 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms of synapse formation and specificity in C. elegans.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019 Jul;76(14):2719-2738. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03109-1. Epub 2019 Apr 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31037336 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ackley B. D., Harrington R. J., Hudson M. L., Williams L., Kenyon C. J., Chisholm A. D. and Jin Y. (2005). The two isoforms of the Caenorhabditis elegans leukocyte-common antigen related receptor tyrosine phosphatase PTP-3 function independently in axon guidance and synapse formation. J. Neurosci. 25, 7517-7528. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2010-05.2005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya R., Touroutine D., Barbagallo B., Climer J. Lambert C. M., Clark C. M., Alkema M. J. and Francis M. M. (2014). A conserved dopamine-cholecystokinin signaling pathway shapes context-dependent Caenorhabditis elegans behavior. PLoS Genet. 10, e1004584 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004584 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

