Factor V has an anticoagulant cofactor activity that targets the early phase of coagulation
- PMID: 28420729
- PMCID: PMC5454113
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.769570
Factor V has an anticoagulant cofactor activity that targets the early phase of coagulation
Abstract
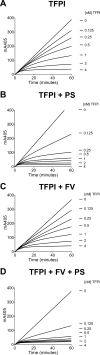
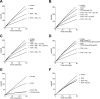
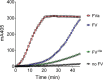
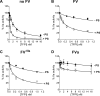
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), the main inhibitor of initiation of coagulation, exerts an important anticoagulant role through the factor Xa (FXa)-dependent inhibition of tissue factor/factor VIIa. Protein S is a TFPI cofactor, enhancing the efficiency of FXa inhibition. TFPI can also inhibit prothrombinase assembly by directly interacting with coagulation factor V (FV), which has been activated by FXa. Because full-length TFPI associates with FV in plasma, we hypothesized that FV may influence TFPI inhibitory function. Using pure component FXa inhibition assays, we found that although FV alone did not influence TFPI-mediated FXa inhibition, it further enhanced TFPI in the presence of protein S, resulting in an ∼8-fold reduction in Ki compared with TFPI alone. A FV variant (R709Q/R1018Q/R1545Q, FVΔIIa) that cannot be cleaved/activated by thrombin or FXa also enhanced TFPI-mediated inhibition of FXa ∼12-fold in the presence of protein S. In contrast, neither activated FV nor recombinant B-domain-deleted FV could enhance TFPI-mediated inhibition of FXa in the presence of protein S, suggesting a functional contribution of the B domain. Using TFPI and protein S variants, we show further that the enhancement of TFPI-mediated FXa inhibition by protein S and FV depends on a direct protein S/TFPI interaction and that the TFPI C-terminal tail is not essential for this enhancement. In FXa-catalyzed prothrombin activation assays, both FV and FVΔIIa (but not activated FV) enhanced TFPI function in the presence of protein S. These results demonstrate a new anticoagulant (cofactor) function of FV that targets the early phase of coagulation before prothrombinase assembly.
Keywords: FV; TFPI; anticoagulant; coagulation factor; enzyme inhibitor; inhibition mechanism; phospholipid; protein S; protein-protein interaction; tissue factor pathway inhibitor.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures

References
-
- Broze G. J. Jr., Warren L. A., Novotny W. F., Higuchi D. A., Girard J. J., and Miletich J. P. (1988) The lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor that inhibits the factor VII-tissue factor complex also inhibits factor Xa: insight into its possible mechanism of action. Blood 71, 335–343 - PubMed
-
- Sanders N. L., Bajaj S. P., Zivelin A., and Rapaport S. I. (1985) Inhibition of tissue factor/factor VIIa activity in plasma requires factor X and an additional plasma component. Blood 66, 204–212 - PubMed
-
- Girard T. J., Warren L. A., Novotny W. F., Likert K. M., Brown S. G., Miletich J. P., and Broze G. J. Jr. (1989) Functional significance of the Kunitz-type inhibitory domains of lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor. Nature 338, 518–520 - PubMed
-
- Baugh R. J., Broze G. J. Jr., and Krishnaswamy S. (1998) Regulation of extrinsic pathway factor Xa formation by tissue factor pathway inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 4378–4386 - PubMed
-
- Huang Z. F., Wun T. C., and Broze G. J. (1993) Kinetics of factor-Xa inhibition by tissue factor pathway inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 26950–26955 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

