Interactive Outlining of Pancreatic Cancer Liver Metastases in Ultrasound Images
- PMID: 28420871
- PMCID: PMC5429849
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00940-z
Interactive Outlining of Pancreatic Cancer Liver Metastases in Ultrasound Images
Abstract
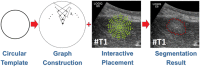
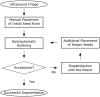
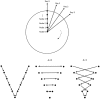
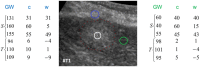
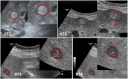
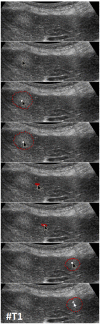
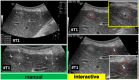
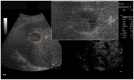
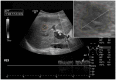
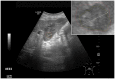
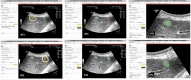
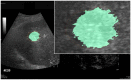
Ultrasound (US) is the most commonly used liver imaging modality worldwide. Due to its low cost, it is increasingly used in the follow-up of cancer patients with metastases localized in the liver. In this contribution, we present the results of an interactive segmentation approach for liver metastases in US acquisitions. A (semi-) automatic segmentation is still very challenging because of the low image quality and the low contrast between the metastasis and the surrounding liver tissue. Thus, the state of the art in clinical practice is still manual measurement and outlining of the metastases in the US images. We tackle the problem by providing an interactive segmentation approach providing real-time feedback of the segmentation results. The approach has been evaluated with typical US acquisitions from the clinical routine, and the datasets consisted of pancreatic cancer metastases. Even for difficult cases, satisfying segmentations results could be achieved because of the interactive real-time behavior of the approach. In total, 40 clinical images have been evaluated with our method by comparing the results against manual ground truth segmentations. This evaluation yielded to an average Dice Score of 85% and an average Hausdorff Distance of 13 pixels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Algorithm guided outlining of 105 pancreatic cancer liver metastases in Ultrasound.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 6;7(1):12779. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12925-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28986569 Free PMC article.
-
RFA-cut: Semi-automatic segmentation of radiofrequency ablation zones with and without needles via optimal s-t-cuts.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015;2015:2423-9. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2015.7318883. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2015. PMID: 26736783
-
Reducing inter-observer variability and interaction time of MR liver volumetry by combining automatic CNN-based liver segmentation and manual corrections.PLoS One. 2019 May 20;14(5):e0217228. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0217228. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31107915 Free PMC article.
-
A state-of-the-art review on segmentation algorithms in intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) images.IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2012 Sep;16(5):823-34. doi: 10.1109/TITB.2012.2189408. Epub 2012 Feb 28. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2012. PMID: 22389156 Review.
-
The latest in ultrasound: three-dimensional imaging. Part 1.Eur J Radiol. 1998 May;27 Suppl 2:S179-82. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(98)00060-6. Eur J Radiol. 1998. PMID: 9652519 Review.
Cited by
-
An Artificial Intelligence Pipeline for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Data to Treatment Recommendations.Int J Gen Med. 2025 Jul 2;18:3581-3595. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S529322. eCollection 2025. Int J Gen Med. 2025. PMID: 40621598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Algorithm guided outlining of 105 pancreatic cancer liver metastases in Ultrasound.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 6;7(1):12779. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12925-z. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28986569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Floriani I, et al. Performance of imaging modalities in diagnosis of liver metastases from colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging 2010 Jan. 2010;31(1):19–31. - PubMed
-
- Seufferlein T, et al. ESMO Guidelines Working Group. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma: ESMO-ESDO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. Suppl. 2012;7:vii33–40. - PubMed
-
- Boen, D. Segmenting 2D Ultrasound Images using Seeded Region Growing. University of British Columbia, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Vancouver, British Columbia, 1–11 (2006).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

