Family and Individual Risk and Protective Factors of Depression among Chinese Migrant Children with Oppositional Defiant Disorder Symptoms
- PMID: 28421024
- PMCID: PMC5378708
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00508
Family and Individual Risk and Protective Factors of Depression among Chinese Migrant Children with Oppositional Defiant Disorder Symptoms
Abstract
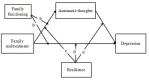
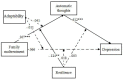
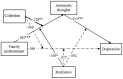
Migrant children reached 35.81 million in China and were vulnerable to serious emotional problems including depression. The present study aimed to identify the family and individual risk and protective factors for depression in an at-risk sample of Chinese migrant children. Participants were 368 children (9.47 ± 1.46 years old, 73.4% boys) who had at least one symptom of Oppositional Defiant Disorder symptoms (ODD) and their parents in Mainland China. Risk and protective factors within both family (i.e., family maltreatment and family functioning) and individual (i.e., automatic thoughts and resilience) perspectives. Family maltreatment and negative automatic thoughts served as risk factors in relation to children's depression. Further, automatic thoughts mediated the relationship between family maltreatment and children's depression. Family functioning (cohesion, but bot adaptability) and individual resilience could buffer the effects of risk factors in the Structure Emotion Model such that both cohesion and resilience moderated the relationship between family maltreatment and children's automatic thoughts only. Our findings highlighted the urgent need to decrease risk factors and increase protective factors of both family and child individual characteristics in prevention and intervention depression among migrant children with ODD symptoms in China.
Keywords: family factors; individual factors; migrant children; oppositional defiant disorder symptoms; protective factors; risk factors.
Figures



References
-
- Aiken L. S., West S. G. (1991). Multiple Regression: Testing and Interpreting Interactions. Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications.
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2013). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edn. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
-
- Beck A. T. (1979). Cognitive Therapy and the Emotional Disorders. New York, NY: Meridian.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

