In Vitro and In Vivo Studies on Quercus acuta Thunb. (Fagaceae) Extract: Active Constituents, Serum Uric Acid Suppression, and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity
- PMID: 28421120
- PMCID: PMC5381200
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/4097195
In Vitro and In Vivo Studies on Quercus acuta Thunb. (Fagaceae) Extract: Active Constituents, Serum Uric Acid Suppression, and Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity
Abstract
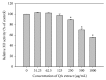
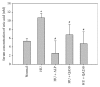
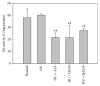
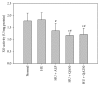
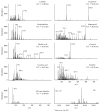
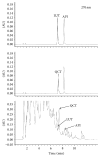
Quercus acuta Thunb. (Fagaceae) (QA) is cultivated as a dietary and ornamental plant in China, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. It has been widely used as the main ingredient of acorn tofu, a traditional food in China and South Korea. The aim of this study was to determine in vitro and in vivo xanthine oxidase (XO) inhibitory and antihyperuricemic activities of an ethyl acetate extract of QA leaf (QALE) and identify its active phytochemicals using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and liquid chromatography (LC) systems. The QALE was found to possess potent in vitro antioxidant and XO inhibitory activities. In vivo study using hyperuricemic mice induced with potassium oxonate demonstrated that the QALE could inhibit hepatic XO activity at a relatively low oral dose (50 mg/kg) and significantly alleviate hyperuricemia to a similar extent as allopurinol. Several active compounds including vitamin E known to possess XO inhibitory activity were identified from the QALE. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that reports the active constituents and antihyperuricemic effect of QA, suggesting that it is feasible to use QALE as a food therapy or alternative medicine for alleviating hyperuricemia and gout.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that there are no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of the biologically active constituents of Camellia japonica leaf and anti-hyperuricemic effect in vitro and in vivo.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Jun;39(6):1613-1620. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2973. Epub 2017 May 3. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28487949
-
Ethanol Extract of Cudrania tricuspidata Leaf Ameliorates Hyperuricemia in Mice via Inhibition of Hepatic and Serum Xanthine Oxidase Activity.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Dec 2;2018:8037925. doi: 10.1155/2018/8037925. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30622611 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of extracts from Corylopsis coreana Uyeki (Hamamelidaceae) flos on xanthine oxidase activity and hyperuricemia.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016 Dec;68(12):1597-1603. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12626. Epub 2016 Oct 2. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27696407
-
Phytochemicals from Tradescantia albiflora Kunth Extracts Reduce Serum Uric Acid Levels in Oxonate-induced Rats.Pharmacogn Mag. 2016 May;12(Suppl 2):S223-7. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.182171. Epub 2016 May 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2016. PMID: 27279711 Free PMC article.
-
An updated patent review: xanthine oxidase inhibitors for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout (2011-2015).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017 Mar;27(3):311-345. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2017.1261111. Epub 2016 Nov 28. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2017. PMID: 27841045 Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effects of Quercus acuta Thunb. fruit extract against UVB-induced photoaging through ERK/AP-1 signaling modulation in human keratinocytes.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022 Jan 4;22(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03473-1. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022. PMID: 34983480 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential and pharmacological mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine in gout treatment.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025 May;46(5):1156-1176. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01459-6. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2025. PMID: 39825190 Review.
-
Identification and Extraction Optimization of Active Constituents in Citrus junos Seib ex TANAKA Peel and Its Biological Evaluation.Molecules. 2019 Feb 14;24(4):680. doi: 10.3390/molecules24040680. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30769817 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Constituents and the Evaluation Biological Effect of Cinnamomum yabunikkei H.Ohba Leaf.Molecules. 2018 Dec 27;24(1):81. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010081. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30591631 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy and Mechanism of Chinese Herbal Medicines in Lowering Serum Uric Acid Levels: A Systematic Review.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jan 25;11:578318. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.578318. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33568990 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhao M., Zhu D., Sun-Waterhouse D., et al. In vitro and in vivo studies on adlay-derived seed extracts: phenolic profiles, antioxidant activities, serum uric acid suppression, and xanthine oxidase inhibitory effects. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2014;62(31):7771–7778. doi: 10.1021/jf501952e. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

