Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Ultrasound Evaluation in Intensive Care Unit: Possible Role and Clinical Aspects in Neurological Critical Patients' Daily Monitoring
- PMID: 28421189
- PMCID: PMC5379077
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/1621428
Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Ultrasound Evaluation in Intensive Care Unit: Possible Role and Clinical Aspects in Neurological Critical Patients' Daily Monitoring
Abstract
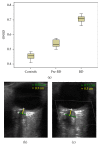
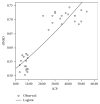
Background. The increase of the optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) is a reliable, noninvasive sonographic marker of intracranial hypertension. Aim of the study was to demonstrate the efficacy of ONSD evaluation, when monitoring neurocritical patients, to early identify malignant intracranial hypertension in patients with brain death (BD). Methods. Data from ultrasound ONSD evaluation have been retrospectively analyzed in 21 sedated critical patients with neurological diseases who, during their clinical course, developed BD. 31 nonneurological controls were used for standard ONSD reference. Results. Patients with neurological diseases, before BD, showed higher ONSD values than control group (CTRL: RT 0.45 ± 0.03 cm; LT 0.45 ± 0.02 cm; pre-BD: RT 0.54 ± 0.02 cm; LT 0.55 ± 0.02 cm; p < 0.000) even without intracranial hypertension, evaluated with invasive monitoring. ONSD was further significantly markedly increased in respect to the pre-BD evaluation in neurocritical patients after BD, with mean values above 0.7 cm (RT 0.7 ± 0.02 cm; LT 0.71 ± 0.02 cm; p < 0.000), with a corresponding dramatic raise in intracranial pressure. Logistic regression analysis showed a strong correlation between ONSD and ICP (R 0,895, p < 0.001). Conclusions. ONSD is a reliable marker of intracranial hypertension, easy to be performed with a minimal training. Routine ONSD daily monitoring could be of help in Intensive Care Units when invasive intracranial pressure monitoring is not available, to early recognize intracranial hypertension and to suspect BD in neurocritical patients.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on "Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Ultrasound Evaluation in Intensive Care Unit: Possible Role and Clinical Aspects in Neurological Critical Patients' Daily Monitoring".Biomed Res Int. 2018 Sep 16;2018:6154357. doi: 10.1155/2018/6154357. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30306088 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Optic nerve sheath diameter measurement: a means of detecting raised ICP in adult traumatic and non-traumatic neurosurgical patients.Am J Emerg Med. 2017 Jan;35(1):150-153. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.09.044. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Am J Emerg Med. 2017. PMID: 27852525
-
Ultrasound non-invasive measurement of intracranial pressure in neurointensive care: A prospective observational study.PLoS Med. 2017 Jul 25;14(7):e1002356. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002356. eCollection 2017 Jul. PLoS Med. 2017. PMID: 28742869 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonographic measured optic nerve sheath diameter as an accurate and quick monitor for changes in intracranial pressure.J Neurosurg. 2015 Sep;123(3):743-7. doi: 10.3171/2014.10.JNS141197. Epub 2015 May 8. J Neurosurg. 2015. PMID: 25955869
-
Using Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter for Intracranial Pressure (ICP) Monitoring in Traumatic Brain Injury: A Scoping Review.Neurocrit Care. 2024 Jun;40(3):1193-1212. doi: 10.1007/s12028-023-01884-1. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Neurocrit Care. 2024. PMID: 38114797 Free PMC article.
-
[Interest of optic nerve sheath diameter ultrasonography in dectecting non-invasively raised intracranial pressure].Neurochirurgie. 2013 Apr;59(2):55-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuchi.2013.02.001. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Neurochirurgie. 2013. PMID: 23523218 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Comment on "Optic Nerve Sheath Diameter Ultrasound Evaluation in Intensive Care Unit: Possible Role and Clinical Aspects in Neurological Critical Patients' Daily Monitoring".Biomed Res Int. 2018 Sep 16;2018:6154357. doi: 10.1155/2018/6154357. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30306088 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Ultrasonographic optic nerve sheath diameter monitoring of elevated intracranial pressure: two case reports.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Jan;8(1):20. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.12.16. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32055611 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound Detection of Intracranial Hypertension in Brain Injuries.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 30;9:870808. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.870808. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35847791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Point-of-care ultrasound in a pandemic: Practical guidance in COVID-19 units.World J Crit Care Med. 2021 Sep 9;10(5):204-219. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v10.i5.204. eCollection 2021 Sep 9. World J Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 34616657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Measurement of corneal thickness, optic nerve sheath diameter and retinal nerve fiber layer as potential new non-invasive methods in assessing a risk of cerebral edema in type 1 diabetes in children.Acta Diabetol. 2018 Dec;55(12):1295-1301. doi: 10.1007/s00592-018-1242-8. Epub 2018 Oct 16. Acta Diabetol. 2018. PMID: 30327872 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dubourg J., Messerer M., Karakitsos D., et al. Individual patient data systematic review and meta-analysis of optic nerve sheath diameter ultrasonography for detecting raised intracranial pressure: protocol of the ONSD research group. Systematic Reviews. 2013;2, article 62 doi: 10.1186/2046-4053-2-62. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

