Detection of (1,3)-β-d-Glucan for the Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Infection in Liver Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 28422065
- PMCID: PMC5412443
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18040862
Detection of (1,3)-β-d-Glucan for the Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Infection in Liver Transplant Recipients
Abstract
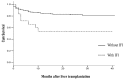
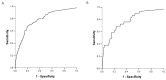
Invasive fungal infections (IFI) are complications after liver transplantation involving high morbidity and mortality. (1,3)-β-d-glucan (BG) is a biomarker for IFI, but its utility remains uncertain. This study was designed to evaluate the impact of BG following their diagnosis. Between January 2013 and May 2016, 271 liver transplants were performed in our institution. Serum samples were tested for BG (Fungitell®, Associates Cape Code Inc., Falmouth, MA, USA) at least weekly between liver transplantation and the discharge of patients. Nineteen patients (7%) were diagnosed with IFI, including 13 cases of invasive candidiasis (IC), eight cases of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis, and one case of septic arthritis due to Scedosporium apiospernum. Using a single BG sample for the primary analysis of IFI, 95% (21/22) of the subjects had positive BG (>80 pg/mL) at the time of IFI diagnosis. The area under the ROC curves to predict IFI was 0.78 (95% CI: 0.73-0.83). The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) of BG for IFI were 75% (95% CI: 65-83), 65% (62-68), 17% (13-21), and 96% (94-97), respectively. Based on their high NPV, the BG test appears to constitute a good biomarker to rule out a diagnosis of IFI.
Keywords: ">d-glucan; (1,3)-β-; invasive candidiasis; invasive fungal infection; invasive pulmonary aspergillosis; liver transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pappas P.G., Alexander B.D., Andes D.R., Hadley S., Kauffman C.A., Freifeld A., Kontoyiannis D.P. Invasive fungal infections among organ transplant recipients: Results of the Transplant-Associated Infection Surveillance Network (TRANSNET) Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010;50:1101–1111. doi: 10.1086/651262. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang C.H., He X.S., Chen J., Ouyang B., Zhu X.F., Chen M.Y., Chen X.X. Fungal infection in patients after liver transplantation in years 2003 to 2012. Ann. Transplant. Q. Pol. Transplant. Soc. 2012;17:59–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

