Economic Burden of Obesity: A Systematic Literature Review
- PMID: 28422077
- PMCID: PMC5409636
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph14040435
Economic Burden of Obesity: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
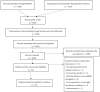
Background: The rising prevalence of obesity represents an important public health issue. An assessment of its costs may be useful in providing recommendations for policy and decision makers. This systematic review aimed to assess the economic burden of obesity and to identify, measure and describe the different obesity-related diseases included in the selected studies. Methods: A systematic literature search of studies in the English language was carried out in Medline (PubMed) and Web of Science databases to select cost-of-illness studies calculating the cost of obesity in a study population aged ≥18 years with obesity, as defined by a body mass index of ≥30 kg/m², for the whole selected country. The time frame for the analysis was January 2011 to September 2016. Results: The included twenty three studies reported a substantial economic burden of obesity in both developed and developing countries. There was considerable heterogeneity in methodological approaches, target populations, study time frames, and perspectives. This prevents an informative comparison between most of the studies. Specifically, there was great variety in the included obesity-related diseases and complications among the studies. Conclusions: There is an urgent need for public health measures to prevent obesity in order to save societal resources. Moreover, international consensus is required on standardized methods to calculate the cost of obesity to improve homogeneity and comparability. This aspect should also be considered when including obesity-related diseases.
Keywords: burden of obesity; cost of illness; obesity; obesity-related disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2000. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Obesity. [(accessed on 4 October 2016)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/topics/obesity/en/
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Overweight & Obesity. [(accessed on 4 October 2016)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/obesity/adult/defining.html.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical