Synthetic Fluororutaecarpine Inhibits Inflammatory Stimuli and Activates Endothelial Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid-Type 1
- PMID: 28422079
- PMCID: PMC6153741
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22040656
Synthetic Fluororutaecarpine Inhibits Inflammatory Stimuli and Activates Endothelial Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid-Type 1
Abstract
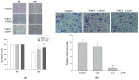
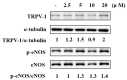
The natural product, rutaecarpine (RUT), is the main effective component of Evodia rutaecarpa which is a widely used traditional Chinese medicine. It has vasodilation, anticoagulation, and anti-inflammatory activities. However, further therapeutic applications are limited by its cytotoxicity. Thus, a derivative of RUT, 10-fluoro-2-methoxyrutaecarpine (F-RUT), was designed and synthesized that showed no cytotoxicity toward RAW264.7 macrophages at 20 μM. In an anti-inflammation experiment, it inhibited the production of nitric oxide (NO) and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages; cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 and inducible NO synthase (iNOS) induced by LPS were also downregulated. After 24 h of treatment, F-RUT significantly inhibited cell migration and invasion of ovarian A2780 cells. Furthermore, F-RUT promoted expressions of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) and endothelial (e)NOS in human aortic endothelial cells, and predominantly reduced the inflammation in ovalbumin/alum-challenged mice. These results suggest that the novel synthetic F-RUT exerts activities against inflammation and vasodilation, while displaying less toxicity than its lead compound.
Keywords: TRPV-1; eNOS; fluoro-rutaecarpine; iNOS; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Rutaecarpine Increases Nitric Oxide Synthesis via eNOS Phosphorylation by TRPV1-Dependent CaMKII and CaMKKβ/AMPK Signaling Pathway in Human Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 30;22(17):9407. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179407. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502308 Free PMC article.
-
Low-cytotoxic synthetic bromorutaecarpine exhibits anti-inflammation and activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 activities.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:795095. doi: 10.1155/2013/795095. Epub 2013 Nov 28. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 24369537 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting MAPK/NF-κB Pathways in Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Rutaecarpine: Impact on Src/FAK-Mediated Macrophage Migration.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 22;23(1):92. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010092. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008520 Free PMC article.
-
Rutaecarpine: A promising cardiovascular protective alkaloid from Evodia rutaecarpa (Wu Zhu Yu).Pharmacol Res. 2019 Mar;141:541-550. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.12.019. Epub 2019 Jan 4. Pharmacol Res. 2019. PMID: 30616017 Review.
-
Evodiamine and rutaecarpine from Tetradium ruticarpum in the treatment of liver diseases.Phytomedicine. 2020 Mar;68:153180. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153180. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Phytomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32092638 Review.
Cited by
-
Promising derivatives of rutaecarpine with diverse pharmacological activities.Front Chem. 2023 Nov 1;11:1199799. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1199799. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2023. PMID: 38025082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorine-Modified Rutaecarpine Exerts Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition and Anti-inflammatory Effects in Lungs.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Feb 7;10:91. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00091. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30792658 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid Type 1 (TRPV1) in the Regulation of Nitric Oxide Release in Wistar Rat Aorta.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Aug 2;2021:8531975. doi: 10.1155/2021/8531975. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34394835 Free PMC article.
-
Transient Receptor Potential Channels and Endothelial Cell Calcium Signaling.Compr Physiol. 2019 Jun 12;9(3):1249-1277. doi: 10.1002/cphy.c180034. Compr Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31187891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rutaecarpine Increases Nitric Oxide Synthesis via eNOS Phosphorylation by TRPV1-Dependent CaMKII and CaMKKβ/AMPK Signaling Pathway in Human Endothelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 30;22(17):9407. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179407. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502308 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gomez-Garre D., Munoz-Pacheco P., Gonzalez-Rubio M.L., Aragoncillo P., Granados R., Fernandez-Cruz A. Ezetimibe reduces plaque inflammation in a rabbit model of atherosclerosis and inhibits monocyte migration in addition to its lipid-lowering effect. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2009;156:1218–1227. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00091.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

