Molecular Imprinting of Macromolecules for Sensor Applications
- PMID: 28422082
- PMCID: PMC5426548
- DOI: 10.3390/s17040898
Molecular Imprinting of Macromolecules for Sensor Applications
Abstract
Molecular recognition has an important role in numerous living systems. One of the most important molecular recognition methods is molecular imprinting, which allows host compounds to recognize and detect several molecules rapidly, sensitively and selectively. Compared to natural systems, molecular imprinting methods have some important features such as low cost, robustness, high recognition ability and long term durability which allows molecularly imprinted polymers to be used in various biotechnological applications, such as chromatography, drug delivery, nanotechnology, and sensor technology. Sensors are important tools because of their ability to figure out a potentially large number of analytical difficulties in various areas with different macromolecular targets. Proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, antibodies, viruses and cells are defined as macromolecules that have wide range of functions are very important. Thus, macromolecules detection has gained great attention in concerning the improvement in most of the studies. The applications of macromolecule imprinted sensors will have a spacious exploration according to the low cost, high specificity and stability. In this review, macromolecules for molecularly imprinted sensor applications are structured according to the definition of molecular imprinting methods, developments in macromolecular imprinting methods, macromolecular imprinted sensors, and conclusions and future perspectives. This chapter follows the latter strategies and focuses on the applications of macromolecular imprinted sensors. This allows discussion on how sensor strategy is brought to solve the macromolecules imprinting.
Keywords: macromolecule; molecular imprinting; sensor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

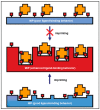

















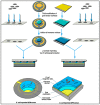



References
-
- Wulff G., Sarhan A. Use of polymers with enzyme analogous structures for the resolution of racemates. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1972;11:341–344.
-
- Wulff G., Gross T., Schonfeld R. Enzyme models based on molecularly imprinted polymers with strong esterase activity. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997;36:1962–1964. doi: 10.1002/anie.199719621. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

