Utilizing combinatorial engineering to develop Tie2 targeting antagonistic angiopoetin-2 ligands as candidates for anti-angiogenesis therapy
- PMID: 28422724
- PMCID: PMC5464891
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16827
Utilizing combinatorial engineering to develop Tie2 targeting antagonistic angiopoetin-2 ligands as candidates for anti-angiogenesis therapy
Abstract
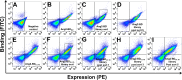
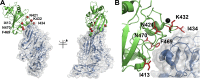
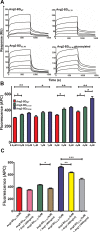
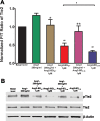
In many human cancers, the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) Tie2 plays important roles in mediating proliferation, survival, migration and angiogenesis. Thus, molecules that could potently inhibit activation of the Tie2 receptor would have a significant impact on cancer therapy. Nevertheless, attempts to develop Tie2-targeted inhibitors have met with little success, and there is currently no FDA-approved therapeutic selectively targeting Tie2. We used a combinatorial protein engineering approach to develop a new generation of angiopoietin (Ang)2-derived Tie2 antagonists as potential cancer therapeutics and as tools to study angiogenesis. The construct for designing a yeast surface display (YSD) library of potential antagonists was an Ang2 binding domain (Ang2-BD) that retains Tie2 binding ability but prevents ligand multimerization and receptor dimerization and activation. This mutant library was then screened by quantitative high-throughput flow cytometric sorting to identify Ang2-BD variants with increased expression, stability and affinity to Tie2. The selected variants were recombinantly expressed and showed high affinity to soluble and cellular Tie2 and strongly inhibited both Tie2 phosphorylation and endothelial capillary tube formation and cell invasion compared to the parental Ang2-BD. The significance of the study lies in the insight it provides into the sequence-structure-function relationships and mechanism of action of the antagonistic Ang mutants. The approach of using a natural protein ligand as a molecular scaffold for engineering high-affinity agents can be applied to other ligands to create functional protein antagonists against additional biomedical targets.
Keywords: angiogenesis; antagonistic activity; directed evolution; protein engineering; protein-protein interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with respect to publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Targeting the Tie2-αvβ3 integrin axis with bi-specific reagents for the inhibition of angiogenesis.BMC Biol. 2018 Aug 17;16(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12915-018-0557-9. BMC Biol. 2018. PMID: 30119679 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic differences in the mechanisms of Tie2 binding to angiopoietins exploited by directed evolution to create an Ang2-selective ligand trap.J Biol Chem. 2021 Aug;297(2):100888. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100888. Epub 2021 Jun 18. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34153320 Free PMC article.
-
A designed angiopoietin-2 variant, pentameric COMP-Ang2, strongly activates Tie2 receptor and stimulates angiogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 May;1793(5):772-80. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2009.01.018. Epub 2009 Feb 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19339208
-
Role of Angiopoietin-2 in Vascular Physiology and Pathophysiology.Cells. 2019 May 17;8(5):471. doi: 10.3390/cells8050471. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31108880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the angiopoietin/Tie2 pathway: cutting tumor vessels with a double-edged sword?J Clin Oncol. 2012 Feb 1;30(4):441-4. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.7621. Epub 2011 Dec 19. J Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22184396 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Engineering Stem Cell Factor Ligands with Different c-Kit Agonistic Potencies.Molecules. 2020 Oct 21;25(20):4850. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204850. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33096693 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Tie2-αvβ3 integrin axis with bi-specific reagents for the inhibition of angiogenesis.BMC Biol. 2018 Aug 17;16(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12915-018-0557-9. BMC Biol. 2018. PMID: 30119679 Free PMC article.
-
All Good Things Must End: Termination of Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signal.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 14;22(12):6342. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126342. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34198477 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Strauss LG, Koczan D, Klippel S, Pan L, Cheng C, Willis S, Haberkorn U, Dimitrakopoulou-Strauss A. Impact of angiogenesis-related gene expression on the tracer kinetics of 18F-FDG in colorectal tumors. J Nucl Med. 2008;49:1238–44. - PubMed
-
- Davis S, Papadopoulos N, Aldrich TH, Maisonpierre PC, Huang T, Kovac L, Xu A, Leidich R, Radziejewska E, Rafique A, Goldberg J, Jain V, Bailey K, et al. Angiopoietins have distinct modular domains essential for receptor binding, dimerization and superclustering. Nat Struct Biol. 2003;10:38–44. - PubMed
-
- Fiedler U, Scharpfenecker M, Koidl S, Hegen A, Grunow V, Schmidt JM, Kriz W, Thurston G, Augustin HG. The Tie-2 ligand angiopoietin-2 is stored in and rapidly released upon stimulation from endothelial cell Weibel-Palade bodies. Blood. 2004;103:4150–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

