The relevance of a low JAK2V617F allele burden in clinical practice: a monocentric study
- PMID: 28422729
- PMCID: PMC5514906
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16744
The relevance of a low JAK2V617F allele burden in clinical practice: a monocentric study
Abstract
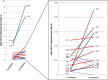
Since low JAK2V617F allele burden (AB) has been detected also in healthy subjects, its clinical interpretation may be challenging in patients with chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs). We tested 1087 subjects for JAK2V617F mutation on suspicion of hematological malignancy. Only 497 (45.7%) patients were positive. Here we present clinical and laboratory parameters of a cohort of 35/497 patients with an AB ≤ 3%.Overall, 22/35 (62.9%) received a WHO-defined diagnosis of MPN and in 14/35 cases (40%) diagnosis was supported by bone marrow (BM) histology (''Histology-based'' diagnosis). In patients that were unable or refused to perform BM evaluation, diagnosis relied on prospective clinical observation (12 cases, 34.3%) and molecular monitoring (6 cases, 17.1%) (''Clinical-based'' or ''Molecular-based'' diagnosis, respectively). In 11/35 (31.4%) patients, a low JAK2V617F AB was not conclusive of MPN. The probability to have a final hematological diagnosis (ET/PV/MF) was higher in patients with thrombocytosis than in patients with polyglobulia (73.7% vs 57.1%, respectively). The detection of AB ≥ 0.8% always corresponded to an overt MPN phenotype. The repetition of JAK2V617F evaluation over time timely detected the spontaneous expansion (11 cases) or reduction (4 cases) of JAK2V617F-positive clones and significantly oriented the diagnostic process.Our study confirms that histology is relevant to discriminate small foci of clonal hematopoiesis with uncertain clinical significance from a full blown disease. Remarkably, our data suggest that a cut-off of AB ≥ 0.8% is very indicative for the presence of a MPN. Monitoring of the AB over time emerged as a convenient and non-invasive method to assess clonal hematopoiesis expansion.
Keywords: JAK2; MPN; V617F mutation; allele burden; myeloproliferative neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lippert E, Boissinot M, Kralovics R, Girodon F, Dobo I, Praloran V, Boiret-Dupré N, Skoda RC, Hermouet S. The JAK2-V617F mutation is frequently present at diagnosis in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Blood. 2006;108:1865–7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-01-013540. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

