Ketamine, as adjuvant analgesics for patients with refractory cancer pain, does affect IL-2/IFN-γ expression of T cells in vitro?: A prospective, randomized, double-blind study
- PMID: 28422864
- PMCID: PMC5406080
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006639
Ketamine, as adjuvant analgesics for patients with refractory cancer pain, does affect IL-2/IFN-γ expression of T cells in vitro?: A prospective, randomized, double-blind study
Abstract
Background: Ketamine has been used as an analgesic adjuvant with morphine in the treatment of refractory cancer pain recently. But both morphine and ketamine have been reported to produce a number of immunomodulatory effects. The current study was performed to assess whether the concentration of ketamine, as adjuvant analgesics for patient with refractory cancer pain, was related to its effect on T cells interleukin-2 (IL-2)/interferon-γ (IFN-γ) expression in vitro.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated from venous blood of patients with refractory cancer pain over a Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient. T cells were isolated from by positive selection using anti-CD3 beads. T cells were then treated with vehicle (C group), morphine (200 ng/mL, M group), morphine (200 ng/mL), and different dose of ketamine (100, 200, 1000 ng/mL; MK1, MK5, MK10 group) for 24 hours before stimulation with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28. Then supernatant IL-2 and IFN-γ protein analysis, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for IL-2 and IFN-γ were done.
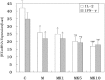
Results: There were no significant difference of supernatant IL-2 and IFN-γ among C group, M group, and MK1 group, but the mRNA of M group and MK1 group were decreased compared with C group (P < .05). Compared with C group, both of the supernatant protein and the mRNA of MK5 group and MK10 group were all significantly decreased (P < .01). Compared with M group, both of the supernatant protein and the mRNA of MK5 group and MK10 group were all decreased (P < .05), while supernatant IL-2 and the mRNA of MK10 group were significantly decreased (P < .01).
Conclusion: In conclusion, we confirmed that just as morphine, ketamine dose-dependently suppressed IL-2 and IFN-γ of activated T lymphocyte of patients with refractory cancer pain in vitro, but the inhibitory action of low dose ketamine could be neglected.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Morphine in Combination with Ketamine Improves Cervical Cancer Pain and Suppresses Immune Function via the JAK3/STAT5 Pathway.Pain Res Manag. 2022 Apr 21;2022:9364365. doi: 10.1155/2022/9364365. eCollection 2022. Pain Res Manag. 2022. PMID: 35492074 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of morphine and a low dose of ketamine on the T cells of patients with refractory cancer pain in vitro.Oncol Lett. 2019 Oct;18(4):4230-4236. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10750. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31516618 Free PMC article.
-
[Interleukin-12 restores and promotes the T-cell immune function inhibited by 5-fluorouracil].Ai Zheng. 2007 Aug;26(8):801-8. Ai Zheng. 2007. PMID: 17697537 Chinese.
-
Antithrombin III inhibits lymphocyte proliferation, immunoglobulin production and mRNA expression of lymphocyte growth factors (IL-2, gamma-IFN and IL-4) in vitro.Transpl Immunol. 2001 Oct;9(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/s0966-3274(01)00042-9. Transpl Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11680566
-
Allergen challenge primes for IL-5 mRNA production and abrogates beta-adrenergic function in peripheral blood T lymphocytes from asthmatics.Clin Exp Allergy. 1999 Jul;29(7):933-40. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.00552.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999. PMID: 10383594
Cited by
-
Perioperative Ketamine and Cancer Recurrence: A Comprehensive Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 26;13(7):1920. doi: 10.3390/jcm13071920. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38610685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphine in Combination with Ketamine Improves Cervical Cancer Pain and Suppresses Immune Function via the JAK3/STAT5 Pathway.Pain Res Manag. 2022 Apr 21;2022:9364365. doi: 10.1155/2022/9364365. eCollection 2022. Pain Res Manag. 2022. PMID: 35492074 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Administration of ketamine/xylazine increases severity of influenza (A/Puerto Rico/8/34) in mice.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 8;9(3):e14368. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14368. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36950568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vadalouca A, Moka E, Argyra E, et al. Opioid rotation in patients with cancer: a review of the current literature. J Opioid Manag 2008;4:213–50. - PubMed
-
- Collins JJ, Grier HE, Kinney HC, et al. Control of severe pain in children with terminal malignancy. J Pediatr 1995;126:653–7. - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz CA, Duncan J, Wolfe J. Caring for the child with cancer at the close of life: “There are people who make it, and I’m hoping I’m one of them”. JAMA 2004;292:2141–9. - PubMed
-
- Jalmsell L, Kreicbergs U, Onelov E, et al. Symptoms affecting children with malignancies during the last month of life: A nationwide follow-up. Pediatrics 2006;117:1314–20. - PubMed
-
- Wolfe J, Grier HE, Klar N, et al. Symptoms and suffering at the end of life in children with cancer. N Engl J Med 2000;342:326–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

