The epidemiology of cryptococcosis and the characterization of Cryptococcus neoformans isolated in a Brazilian University Hospital
- PMID: 28423088
- PMCID: PMC5398185
- DOI: 10.1590/S1678-9946201759013
The epidemiology of cryptococcosis and the characterization of Cryptococcus neoformans isolated in a Brazilian University Hospital
Abstract
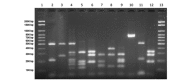
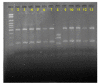
Cryptococcosis, a systemic disease caused by the fungus Cryptococcus neoformans/ Cryptococcus gattii is more severe in immunocompromised individuals. This study aimed to analyze the epidemiology of the disease, the molecular characteristics and the antifungal susceptibility of C. neoformans isolated from patients treated in a Brazilian university hospital. This retrospective study was conducted in the Clinical Hospital, Federal University of Uberlândia, and evaluated cases of cryptococcosis and strains of C. neoformans isolated from 2004 to 2013. We evaluated 41 patients, 85% of whom were diagnosed with AIDS. The fungus was isolated from the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of 21 patients (51%); 19.5% had fungemia and in 24% the agent was isolated from the CSF and blood, concurrently. Meningoencephalitis was the most frequent (75%) manifestation of infection. Despite adequate treatment, the mortality of the disease was 58.5%. Most isolates (97.5%) presented the VNI genotype (serotype A, var. grubii) and one isolate was genotyped as C. gattii (VGI); all the isolates were determined as mating type MATa and showed susceptibility to the tested antifungals (fluconazole, voriconazole, amphotericin B and 5-flucytosine). Although AIDS detection rates remain stable, opportunistic infections such as cryptococcosis remain as major causes of morbidity and mortality in these patients.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS None.
Figures
References
-
- Lacaz CS, Porto E, Martins JE, Heins-Vaccari EM, Melo NT. Lacaz CS. Tratado de micologia médica. 9. São Paulo: Sarvier; 2002. Criptococose.
-
- Pappalardo MC, Melhem MS. Cryptococcosis a review of the Brazilian experience for the disease. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2003;45:299–305. - PubMed
-
- Park BJ, Wannemuehler KA, Marston BJ, Govender N, Pappas PG, Chiller TM. Estimation of the current global burden of cryptococcal meningitis among persons living with HIV/AIDS. AIDS. 2009;23:525–530. - PubMed
-
- Bicanic T, Harrison TS. Cryptococcal meningitis. Br Med Bull. 2005;72:99–118. - PubMed
-
- Kwon-Chung KJ, Varma A. Do major species concepts support one, two or more species within Cryptococcus neoformans. FEMS Yeast Res. 2006;6:574–587. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

