MicroRNA-34a targets epithelial to mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors (EMT-TFs) and inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion
- PMID: 28423483
- PMCID: PMC5400590
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15214
MicroRNA-34a targets epithelial to mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors (EMT-TFs) and inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion
Abstract
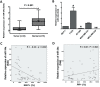
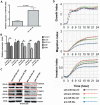
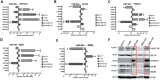
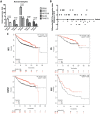
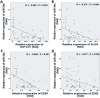
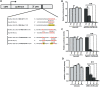
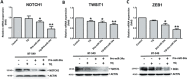
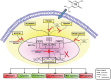
MicroRNA-34a (miR-34a) plays an essential role against tumorigenesis and progression of cancer metastasis. Here, we analyzed the expression, targets and functional effects of miR-34a on epithelial to mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription factors (EMT-TFs), such as TWIST1, SLUG and ZEB1/2, and an EMT-inducing protein NOTCH1 in breast cancer (BC) cell migration and invasion and its correlation with tumorigenesis and clinical outcomes. Expression of miR-34a is downregulated in human metastatic breast cancers (MBC) compared to normal breast tissues and is negatively correlated with clinicopathological features of MBC patients. Ectopic expression of miR-34a in MBC cell-line BT-549 significantly inhibits cell migration and invasion, but exhibits no clear effect on BC cell growth. We found that miR-34a is able to inactivate EMT signaling pathway with mediatory of NOTCH1, TWIST1, and ZEB1 upon 3'-UTR activity in MBC cell lines, but has no inhibitory effects on SLUG and ZEB2. Furthermore, we investigated the synergistic effects of Thymoquinone (TQ) and miR-34a together on the expression of EMT-associated proteins. Results showed that co-delivery of miR-34a and TQ is able to inactivate EMT signaling pathway by directly targeting TWIST1 and ZEB1 in BT-549 cell line, indicating that they might be a promising therapeutic combination against breast cancer metastasis. Epigenetic inactivation of the EMT-TFs/miR-34a pathway can potentially alter the equilibrium of these regulations, facilitating EMT and metastasis in BC. Altogether, our findings suggest that miR-34a alone could serve as a potential therapeutic agent for MBC, and together with TQ, their therapeutic potential is synergistically enhanced.
Keywords: breast cancer; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; metastasis; microRNA-34a; thymoquinone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflicts of interest that perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
53BP1 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition by downregulating ZEB1 through microRNA-200b/429 in breast cancer.Cancer Sci. 2015 Aug;106(8):982-9. doi: 10.1111/cas.12699. Epub 2015 Jul 14. Cancer Sci. 2015. PMID: 26011542 Free PMC article.
-
Thymoquinone inhibits cancer metastasis by downregulating TWIST1 expression to reduce epithelial to mesenchymal transition.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 14;6(23):19580-91. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3973. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26023736 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of breast cancer metastatic behavior by microRNAs targeting EMT transcription factors. A relevant participation of miR-196a-5p and miR-22-3p in ZEB1 expression.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025 Jul;212(2):277-290. doi: 10.1007/s10549-025-07723-5. Epub 2025 May 18. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2025. PMID: 40382762
-
Prognostic Value of EMT-inducing Transcription Factors (EMT-TFs) in Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 23;6:28587. doi: 10.1038/srep28587. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27335258 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay Between Transcription Factors and MicroRNAs Regulating Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transitions in Colorectal Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;937:71-92. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-42059-2_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 27573895 Review.
Cited by
-
Restoring microRNA-34a overcomes acquired drug resistance and disease progression in human breast cancer cell lines via suppressing the ABCC1 gene.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Feb;204(1):133-149. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-07170-0. Epub 2023 Dec 7. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38057687 Free PMC article.
-
TSPAN9 and EMILIN1 synergistically inhibit the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by increasing TSPAN9 expression.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jun 26;19(1):630. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5810-2. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31242895 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of miR-34a-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Non-Small Lung Cancer Cells Focusing on p53.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 9;11(12):1853. doi: 10.3390/biom11121853. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944497 Free PMC article.
-
SOX9 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the Hippo-YAP signaling pathway in gastric carcinoma cells.Oncol Lett. 2019 Jul;18(1):599-608. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10387. Epub 2019 May 21. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31289532 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-34a: A Versatile Regulator of Myriads of Targets in Different Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Oct 2;18(10):2089. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102089. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29036883 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Umemura S, Sakamoto G, Sasano H, Tsuda H, Akiyama F, Kurosumi M, Tokuda Y, Watanabe T, Toi M, Hasegawa T, Osamura RY. Evaluation of HER2 status: for the treatment of metastatic breast cancers by humanized anti-HER2 Monoclonal antibody (trastuzumab) (Pathological committee for optimal use of trastuzumab) Breast Cancer. 2001;8:316–20. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

